Introduction
AI voice over refers to the generation of spoken audio using artificial intelligence rather than a human recording session.
Instead of capturing a person’s voice through a microphone, AI voice systems convert written text into speech by predicting how language should sound based on learned patterns.
This technology has moved far beyond early robotic text-to-speech and is now used across media, software, education, and accessibility tools. As a result, many people encounter AI-generated voices daily without realizing it.
This article explains what AI voice over is, how it works at a high level, and why it has become a foundational technology in modern digital content.
Key Takeaways
- AI voice over is the generation of spoken audio from text using artificial intelligence rather than human recording.
- Modern AI voice systems create speech by modeling language patterns, timing, and pronunciation, not by replaying stored recordings.
- Unlike traditional voice over, AI voice allows narration to be generated, updated, and reused without new recording sessions.
- AI voice over is a category of technology, not a single tool, and includes several related terms such as text-to-speech and synthetic voice.
- The widespread use of AI voice is driven by its flexibility, consistency, and ability to scale across digital content.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.
What Is AI Voice Over?
AI voice over is the use of artificial intelligence to generate spoken audio from written text without recording a human speaker. Instead of capturing a voice through a microphone, an AI system produces speech by modeling how words, sounds, and rhythms typically come together in natural language. The result is audio that functions like a traditional voice over, but is created entirely through software.
In practical terms, AI voice over allows written content to be turned into narration on demand. A script, article, or set of instructions becomes spoken audio without scheduling a recording session or working with a live narrator. This makes voice a repeatable, editable output rather than a one-time performance.
AI voice over is best understood as a category of technology, not a single tool or product. Different systems vary in how they generate speech, how natural they sound, and how much control they offer, but they all share the same core purpose: transforming text into spoken language through automated means.

How AI Voice Over Works at a High Level
At a high level, AI voice over works by converting written text into spoken audio through pattern recognition rather than human recording. An AI system is trained on large amounts of speech data so it can learn how words, sounds, and timing typically relate to one another. When new text is provided, the system predicts how that text should sound when spoken aloud.
The process generally begins with text analysis. The system breaks sentences into smaller components, such as words and sounds, and determines pronunciation, emphasis, and pacing. It then generates an audio signal that follows those patterns, producing speech that aligns with natural language rhythms rather than reading words one by one.
Modern AI voice systems differ from early text-to-speech because they model speech as a continuous flow instead of a sequence of disconnected sounds. This allows them to produce smoother transitions, more natural pauses, and more consistent intonation. While the underlying technology can be complex, the outcome is simple: written language becomes spoken audio without the need for a live narrator.
Core Terms Used in AI Voice Technology
AI voice over is often described using overlapping terms, which can make the category feel more complex than it is. While these phrases are sometimes used interchangeably, they usually refer to slightly different aspects of the same underlying process. Understanding how these terms relate helps clarify what AI voice systems actually do.
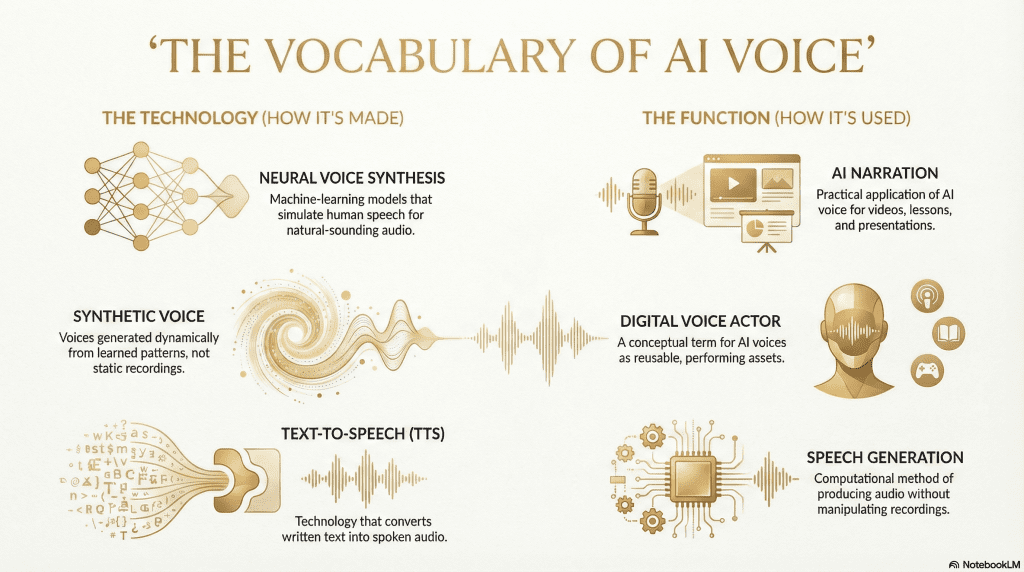
Text-to-speech (TTS) refers to the general process of converting written text into spoken audio. It is the broad category that includes both early, rule-based systems and modern AI-driven approaches. When people talk about AI voice over, they are typically referring to advanced forms of text-to-speech.
A synthetic voice is a voice that is generated rather than recorded. Instead of replaying stored audio clips, the system produces speech dynamically based on learned patterns. This allows the same voice to read new text without additional recording.
Neural voice synthesis describes the use of machine-learning models that simulate how humans produce speech. These models generate audio as a continuous signal, which helps create smoother transitions, more natural pacing, and consistent tone.
Speech generation is a general term for producing spoken audio through computational methods. In the context of AI voice, it usually refers to systems that generate speech from text rather than manipulating existing recordings.
AI narration emphasizes how the voice is used rather than how it is created. It refers to AI-generated speech applied to narration tasks such as videos, lessons, or presentations.
A digital voice actor is a conceptual term used to describe an AI voice that performs the role traditionally filled by a human narrator. It highlights function rather than technology, framing the voice as a reusable asset rather than a one-time performance.
How AI Voice Over Differs From Traditional Voice Over
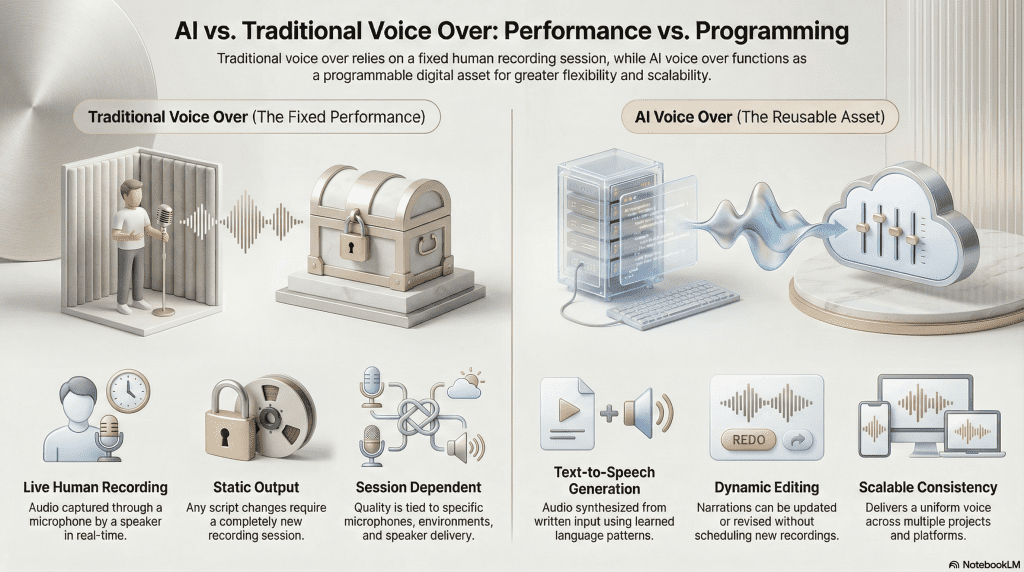
Traditional voice over is created by recording a human speaker reading a script in real time. The voice exists as a fixed performance, captured through a microphone and shaped by the speaker’s delivery, environment, and recording conditions. Any change to the script usually requires the speaker to return and record the audio again.
AI voice over follows a different process. Instead of recording a performance, the voice is generated when needed based on written input. The same underlying voice can read new or revised text without additional recording sessions, making the output easier to update, reuse, or adapt over time.
Another key difference is how voice is treated as an asset. In traditional voice over, each recording is tied to a specific session and script. With AI voice over, the voice itself can function as a reusable digital resource that produces consistent narration across many pieces of content.
These differences do not imply that one approach replaces the other. Traditional and AI voice over exist as separate categories, each suited to different needs depending on context, expectations, and constraints.
Common Misunderstandings About AI Voice Over
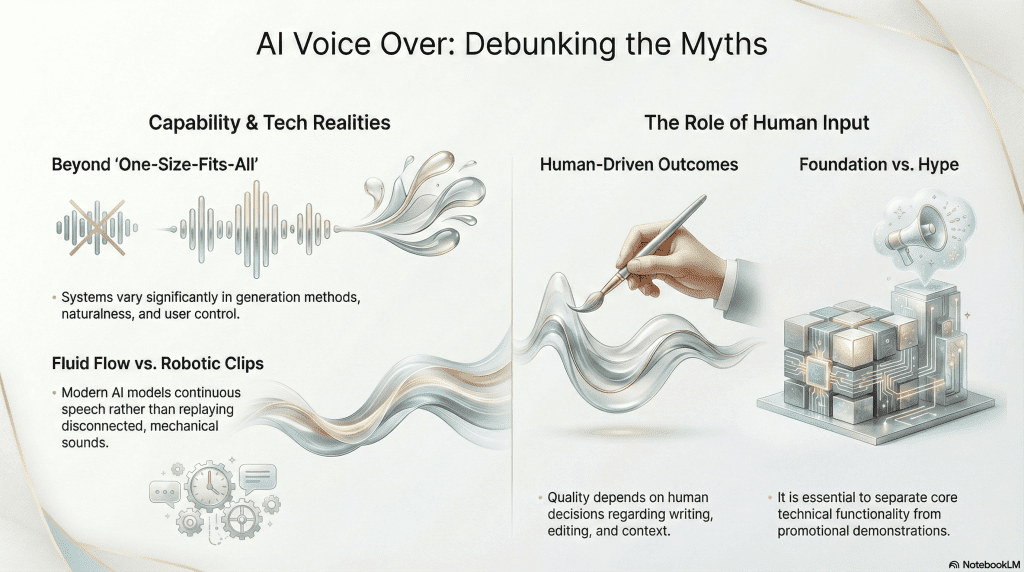
As AI voice over has become more visible, the way it is discussed has not always kept pace with how the technology actually works. One common misunderstanding is treating all AI voices as essentially the same. In reality, AI voice systems vary widely in how speech is generated, how natural it sounds, and how much control is possible, even when they appear similar on the surface.
Another frequent source of confusion is associating modern AI voice over with early text-to-speech experiences. Many people still picture rigid, mechanical audio when they hear the term, even though contemporary systems generate speech as a continuous flow rather than a sequence of fixed sounds. This makes modern AI voice fundamentally different from earlier approaches.
AI voice over is also sometimes misunderstood as a fully autonomous replacement for human involvement. While speech generation itself is automated, humans still shape outcomes through writing, editing, and contextual decisions. The quality of the result often depends as much on how the voice is used as on the technology producing it.
Finally, discussions about AI voice over often blend explanation with promotion. Examples and demonstrations may emphasize possibilities without clearly separating foundational understanding from evaluation or comparison. Recognizing this distinction helps keep learning about the category grounded and accurate.
⚠️ The Ethics of Voice Cloning
A common confusion is the difference between generating a new voice and cloning an existing one.
- Generation (Safe): Creating a unique synthetic voice from a dataset of many speakers. This is standard for most content creation.
- Cloning (Restricted): Using AI to mimic a specific person’s voice (like a celebrity or politician).
The Golden Rule: Legitimate AI voice platforms require express consent to clone a voice. Using AI to mimic a person without their permission is not just an ethical violation, it is increasingly illegal in many jurisdictions.
Why AI Voice Over Has Become Widely Used
AI voice over has become widely used because it changes how spoken audio can be created and maintained over time. Instead of treating narration as a fixed recording, AI systems allow voice to be generated whenever it is needed, making updates and revisions easier to manage. This flexibility is especially useful in environments where content changes frequently or must be produced at scale.
Another factor is consistency. AI voice over can deliver the same voice across many pieces of content without variation caused by different recording sessions, speakers, or environments. This makes it easier to maintain a uniform listening experience across videos, courses, applications, and other formats.
Accessibility has also played a role in adoption. AI-generated voices make it possible to turn written content into audio quickly, supporting audiences who prefer or rely on spoken information. As digital content has expanded across platforms and regions, the ability to generate voice efficiently has become increasingly practical.
Together, these factors have positioned AI voice over as a foundational layer in modern content creation and software experiences. Rather than replacing existing approaches, it has added a new way to produce spoken audio that aligns with the speed and scale of digital communication.
💡 Where You Have Already Heard AI Voice
You likely encounter AI voice over daily without realizing it. Common examples include:
- Social Media: The viral narrators on TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts.
- Audiobooks: Apple Books and Audible now use “Digital Narration” for specific back-catalog titles.
- Customer Service: The natural-sounding bots you speak to when calling airlines or banks.
Corporate Training: Internal HR videos and safety briefings where the script changes frequently.

Conclusion
AI voice over is best understood as a way of generating spoken audio through software rather than recording a human performance.
By converting text into speech using learned language patterns, it allows voice to function as a flexible and reusable part of digital content. This shift has made it easier to produce, update, and maintain narration across many formats and platforms.
Understanding how AI voice over works at a foundational level helps clarify why it appears in so many modern experiences, often without being noticed. It also provides the context needed to evaluate related topics such as voice quality, ethical use, and practical applications.
With a clear mental model of what AI voice over is and why it exists, the technology becomes easier to assess thoughtfully as it continues to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is AI voice over the same as text-to-speech?
AI voice over is a modern form of text-to-speech, but the terms are not always identical. Text-to-speech refers broadly to converting written text into spoken audio, including older, rule-based systems. AI voice over usually describes newer approaches that use machine learning to produce more natural and fluid speech.
Are AI voices recorded or generated?
AI voices are generated rather than recorded. While systems may be trained on recorded speech, the final audio is created dynamically based on patterns the model has learned. This allows the same voice to read new text without recording additional audio.
Can AI voice over sound natural?
AI voice over can sound increasingly natural because modern systems model speech as a continuous flow instead of isolated sounds. Factors such as timing, emphasis, and intonation contribute to how natural a voice feels. Perceived realism can vary depending on the system and how it is used.
Is AI voice over always fully automated?
AI voice over is generated automatically, but humans are often involved in writing scripts, adjusting settings, or reviewing output. Automation refers to how the audio is produced, not the absence of human decision-making in the overall process.
Where is AI voice over commonly used today?
AI voice over is used across many contexts, including videos, educational materials, software interfaces, accessibility tools, and digital media. In many cases, people interact with AI-generated voices without actively noticing them.
Why do people refer to AI voices as “digital voice actors”?
The term “digital voice actor” is used to describe the role an AI voice plays rather than its technical construction. It reflects how AI-generated voices can perform narration consistently across multiple projects, similar to how a human voice actor might be hired for repeated work.
0 Comments