Introduction
A/B testing is a simple way to compare two versions of a page, email, or ad to see which one performs better. It replaces guesswork with data, which makes every change more intentional and more reliable.
Many people struggle with testing because they are unsure where to start or what to test first. Others try to test everything at once and end up with results they cannot trust.
A clear A/B test shows you what works, what does not, and why. It helps you improve conversions, refine your message, and understand how people respond to your choices.
This guide explains what A/B testing is, how it works, and how to use it effectively without overcomplicating the process.
For a full glossary of marketing terms, visit our Marketing Glossary Page.
Key Takeaways
- A/B testing compares two versions to determine which performs better against a specific goal.
- Reliable tests focus on one variable at a time and use clear success metrics.
- Letting tests run long enough is critical for trustworthy results.
- High-impact elements like headlines and calls to action deliver the most value.
- Consistent testing leads to better decisions and long-term performance gains.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.
What A/B Testing Is
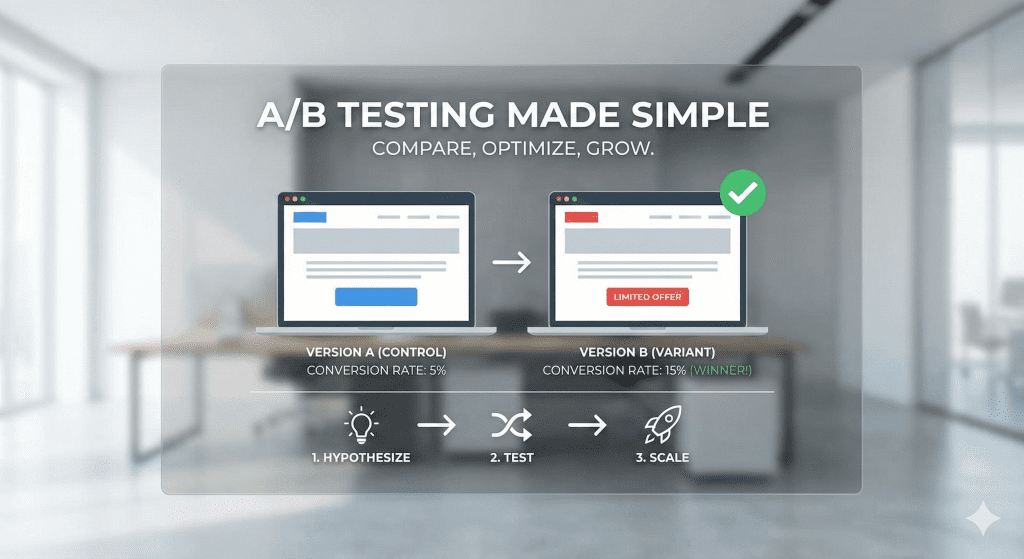
A/B testing is a method used to compare two versions of the same asset to see which one performs better against a defined goal. One version is the original, often called the control. The other version includes a single, intentional change and is known as the variation.
Both versions are shown to different segments of the audience at the same time. Because the audience is split, the results reflect how real users respond, not how the creator expects them to respond. This makes A/B testing a practical way to evaluate decisions using evidence rather than instinct.
At its core, A/B testing is about isolating cause and effect. If only one element changes between the two versions, any meaningful difference in performance can be attributed to that change. This is what separates A/B testing from casual experimentation or guesswork.
It is also important to understand what A/B testing is not. It is not testing multiple changes at once. It is not redesigning an entire page and hoping for the best. And it is not a one-time activity meant to deliver a permanent answer. A/B testing is a controlled comparison designed to answer one clear question at a time.
When used this way, A/B testing becomes a reliable decision-making tool. It helps teams learn how people actually behave, not how they think they will behave. That understanding is what makes testing valuable across websites, emails, ads, and product experiences.

Why A/B Testing Matters
Most decisions in marketing and product design start as assumptions. A headline feels strong. A layout looks clear. A call to action seems obvious. Until those ideas are tested, they remain guesses.
A/B testing matters because it replaces opinion with evidence. Instead of debating what should work, you can measure what actually does. This leads to decisions that are easier to justify and easier to repeat.
Testing also reduces risk. Making changes without data can hurt performance without warning. A/B testing lets you validate ideas on a smaller scale before applying them broadly. If a change improves results, you keep it. If it does not, you learn without causing long-term damage.
Another reason A/B testing matters is consistency. One successful test may improve a single page, but repeated testing builds patterns. Over time, you learn how your audience responds to language, structure, and offers. Those insights can be applied across pages, campaigns, and channels.
Most importantly, A/B testing supports steady improvement. You do not need one dramatic win to see value. Small, proven changes compound. Each test adds clarity, and that clarity leads to better performance decisions over time.
How A/B Testing Works
A/B testing works by showing two versions of the same asset to different segments of your audience and measuring how each version performs against a specific goal. The key is that both versions run at the same time under the same conditions.
Version A is the control. It represents the current or original version. Version B is the variation. It includes one deliberate change, such as a different headline, button label, or layout adjustment. By changing only one element, you can isolate what caused any difference in results.
Traffic or users are split evenly between the two versions. This split reduces bias and ensures that performance differences come from the change itself, not from who happened to see the page or message first. The test continues until enough data is collected to make a meaningful comparison.
Performance is measured using a predefined metric tied to your goal. This could be clicks, signups, purchases, or another clear action. The version that performs better against that metric is considered the stronger option.
What makes this process effective is control. By keeping everything the same except for one variable, A/B testing creates a clear cause-and-effect relationship. This structure is what allows you to trust the outcome and apply the result with confidence.
The Step-by-Step A/B Testing Process
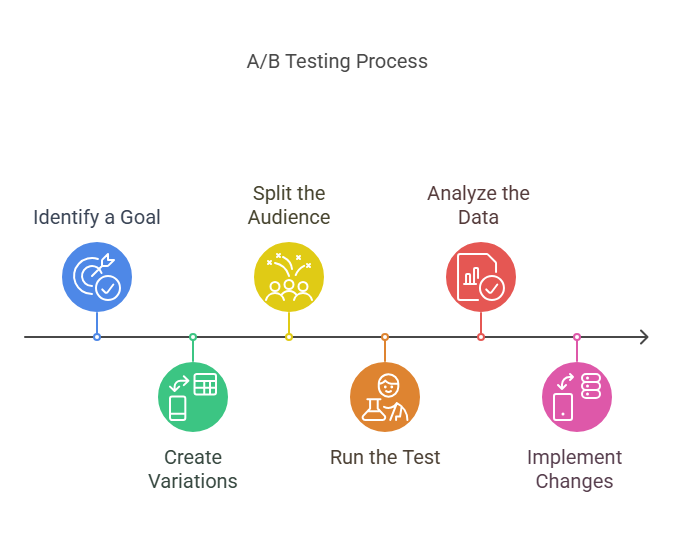
A clean A/B test follows a clear sequence. Skipping steps or changing the order makes results harder to trust. When each step is handled deliberately, the outcome becomes easier to interpret and apply.
1. Define the goal
Start with one clear objective. This could be increasing signups, improving click-through rates, or driving purchases. A single goal keeps the test focused and prevents conflicting interpretations later.
2. Choose one variable to test
Select one element to change. This might be a headline, a call to action, an image, or a layout adjustment. Limiting the test to one variable ensures that any performance difference has a clear cause.
3. Create the variation
Build the alternate version with only the selected change applied. Everything else should remain identical to the control. This consistency is what allows for a fair comparison.
4. Split traffic evenly
Send an equal share of users to each version. An even split reduces bias and ensures that results are driven by the variation, not by differences in audience behavior.
5. Run the test long enough
Let the test collect sufficient data. Ending too early can produce misleading results. The test should run until performance patterns stabilize and enough users have interacted with both versions.
6. Compare results against the goal
Evaluate performance using the metric defined at the start. The version that performs better against that goal provides the insight. Apply the winning version, document the learning, and use it to guide future tests.
Following this process keeps testing disciplined. Each step supports clarity, and that clarity is what makes A/B testing a reliable decision-making tool.

What to Test (and What to Avoid Testing)
Not every element is worth testing. A/B testing delivers the most value when you focus on changes that influence how people understand your message and decide to act. Testing the wrong elements can waste time and produce results that do not improve performance.
High-impact elements to test first
These elements shape attention and decision making. Small changes here can lead to meaningful improvements.
- Headlines that define the main message
- Primary calls to action that guide the next step
- Page layout that affects how quickly key information is found
- Offer framing that influences perceived value
Because these elements sit at the center of the experience, testing them often produces clear, actionable insights.
Mid-impact elements worth testing after
These elements support clarity and usability. They can improve results, but usually after high-impact areas are addressed.
- Images that reinforce the message
- Button text that clarifies intent
- Color contrast that improves visibility
- Form length that affects completion rates
These tests are most effective when the core message and structure are already strong.
What to avoid testing
Some tests create noise without adding insight.
- Micro changes that most users do not notice
- Elements unrelated to the primary goal
- Multiple changes bundled into a single test
- Tweaks that disrupt the overall flow or context
Avoiding low-impact or misleading tests keeps your testing program focused. When each test targets an element that truly matters, the results become easier to trust and more useful to apply.
When A/B Testing Makes Sense
A/B testing is most effective when there is enough activity to support meaningful comparison. Without sufficient data, results can be misleading or inconclusive. Understanding when testing adds value helps you avoid wasted effort.
A/B testing makes sense when you have steady traffic or engagement. Pages, emails, or ads that receive regular visits provide enough interactions to compare versions reliably. The more consistent the activity, the easier it is to detect real performance differences.
It is also useful when you have a clear goal. Testing works best when success is defined upfront, such as increasing signups, clicks, or purchases. A clear objective keeps the test focused and makes the outcome easier to evaluate.
A/B testing is less effective when traffic is very low or when changes are frequent and uncontrolled. If a page is still being redesigned or a campaign is constantly shifting, testing can add noise rather than insight. In these cases, it is better to stabilize the experience first.
Testing also may not be necessary for obvious fixes. If a form is broken or a message is unclear, correcting the issue does not require a test. A/B testing is best reserved for decisions where multiple reasonable options exist and data can guide the choice.
Used in the right situations, A/B testing provides clarity and confidence. Used at the wrong time, it can slow progress and create false signals.
A Simple A/B Testing Example
Imagine a landing page that offers a free downloadable guide. The page receives steady traffic, but the signup rate feels lower than expected. The goal is to increase the number of people who complete the form.
The situation
The page headline explains the guide, but it is long and descriptive. Visitors scroll the page, but many leave without signing up.
The hypothesis
A shorter, more direct headline will make the value clearer and increase signups.
The test
- Version A keeps the original headline.
- Version B uses a shorter headline that focuses on the main benefit. Everything else on the page remains the same.
Traffic is split evenly between both versions, and the test runs long enough to collect reliable data.
The result
Version B produces a higher signup rate. More visitors understand the offer quickly and take action.
The insight
Clear, benefit-focused headlines perform better for this audience. That insight can now be applied to other landing pages and campaigns.
This example shows the value of testing one clear idea at a time. The goal was specific, the change was focused, and the result provided a lesson that could be reused elsewhere.

Common A/B Testing Mistakes
A/B testing can produce misleading results when the process is rushed or poorly structured. Many failed tests are not caused by bad ideas, but by avoidable execution errors.
Testing multiple variables at once
Changing more than one element in a single test makes it impossible to identify what influenced the result. Even if performance improves, you cannot know which change caused it. Clean tests isolate one variable at a time.
Ending tests too early
Early performance often fluctuates. Stopping a test before enough data is collected can lead to false conclusions. Reliable results require patience and sufficient volume.
Using sample sizes that are too small
Small audiences can create dramatic swings that do not reflect real behavior. A larger sample produces more stable and trustworthy comparisons.
Focusing on the wrong metric
Not every metric reflects success. Measuring page views or time on page may look interesting but may not align with the goal. Each test should be evaluated against a single outcome that matters.
Ignoring context and user flow
A test may improve one step but hurt the overall experience. Always consider how the change fits within the full journey. A result is only valuable if it supports the broader goal.
Avoiding these mistakes helps ensure that each test produces insights you can trust and apply with confidence.

A/B Testing Tools by Use Case
A/B testing does not require complex software to be effective. The right tool depends on where you are testing and how much control or insight you need. Most tools fall into a few clear categories.
Website and landing page tools
These tools allow you to create page variations and split traffic automatically. They are useful when testing headlines, layouts, calls to action, or page structure. Many website builders include basic A/B testing features, which makes them a practical option for simple tests and faster setup.
Email marketing platforms
Most email platforms offer built-in A/B testing. You can test subject lines, content blocks, calls to action, or sending times. Email testing works well because results appear quickly and success metrics like opens and clicks are easy to track.
Advertising platforms
Ad platforms make testing part of the campaign setup. You can test different headlines, images, or creative formats while the platform handles audience distribution. These tests help identify which message performs best before sending traffic to a landing page.
Dedicated testing platforms
These tools provide deeper analysis and more control. They are useful for larger sites or teams that want detailed insight into user behavior. While more powerful, they also require more setup and planning.
The best tool is the one that fits your current needs and traffic level. Starting simple is often more effective than adopting advanced tools too early.

Conclusion
A/B testing gives you a reliable way to improve performance without relying on assumptions. By comparing two versions under the same conditions, you can see how real users respond and make decisions based on evidence rather than opinion.
The value of A/B testing does not come from complex tools or dramatic changes. It comes from focus. One clear goal. One intentional change. Enough data to trust the outcome. When those elements are in place, testing becomes a dependable part of decision making.
Over time, small improvements compound. Each test adds insight into how your audience thinks, reacts, and chooses to act. When A/B testing is treated as an ongoing practice rather than a one-time experiment, it creates clarity, confidence, and more predictable results across your pages, emails, and campaigns.

Frequently Asked Questions
How long should an A/B test run?
An A/B test should run long enough to collect a meaningful amount of data. This usually means several days or weeks, depending on traffic volume. Ending a test too early can lead to unreliable conclusions.
What is a good sample size for A/B testing?
There is no single number that fits every test. Each version should receive enough traffic to show a clear performance pattern. Larger samples reduce the chance of misleading results.
Can beginners run A/B tests without advanced tools?
Yes. Many website builders, email platforms, and ad tools include basic A/B testing features. You can run effective tests without technical expertise or complex software.
Is A/B testing only useful for websites?
No. A/B testing can be applied to emails, ads, landing pages, sign-up forms, checkout flows, and other parts of the user experience. The process stays the same across channels.
Should I test large changes or small changes first?
Start with elements that directly influence the goal, such as headlines, calls to action, or page structure. These often create the most meaningful impact before smaller refinements.
How do I know if my test results are reliable?
Reliable tests have one variable, a clear goal, enough data, and a consistent testing environment. When these conditions are met, the results are easier to trust and apply.
3 Comments
ClickFunnels vs Leadpages: The Brutally Honest 2025 Showdown - Ismel Guerrero. · March 23, 2025 at 9:59 pm
[…] A/B Testing Strategies for Beginners Test one element at a time—like a headline, CTA button, or offer format—for clearer data. […]
High-Converting Landing Pages to Maximize Results - Ismel Guerrero. · July 5, 2025 at 8:54 am
[…] Check out our A/B Testing Guide. […]
Conversion Rate Optimization: Step-by-Step Guide - Ismel Guerrero. · March 3, 2026 at 6:49 pm
[…] A/B testing, multivariate testing, and user behavior […]