Introduction
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is one of the most crucial performance metrics in digital advertising.
It measures how much revenue is generated for every dollar spent on ads, helping businesses determine whether their marketing efforts are profitable or need optimization.
A high return on ad spend indicates that an advertising campaign is effective, while a low ROAS suggests that adjustments are needed.
But what actually influences ROAS, and how can you improve it to maximize profitability?
This article will break down the key factors affecting ROAS and provide actionable strategies to help you boost your ad efficiency.

Key Takeaways
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
- A high ROAS means profitable campaigns, while a low ROAS signals inefficiencies.
- Key factors that influence ROAS include audience targeting, ad creatives, bidding strategies, landing page optimization, and market trends.
- Businesses can improve ROAS through better targeting, A/B testing, budget optimization, and retargeting strategies.
- Tracking ROAS regularly helps businesses make data-driven decisions and maximize ad profitability.
What is Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)?
ROAS, or Return on Ad Spend, is a crucial metric that shows how effectively an advertising campaign generates revenue relative to its cost. The formula is straightforward:
ROAS = Revenue from Ads / Cost of Ads
For instance, if you invest $1,000 in ads and generate $5,000 in revenue, your ROAS would be 5:1, meaning that for every dollar spent, you earn $5 back.
A higher return on ad spend signifies that your advertising is driving strong revenue, while a lower ROAS may indicate inefficiencies in your targeting, ad creatives, or budget allocation.
Unlike general profit metrics, ROAS focuses specifically on ad performance, making it an essential tool for optimizing marketing strategies and maximizing returns.
Factors That Influence Return on Ad Spend
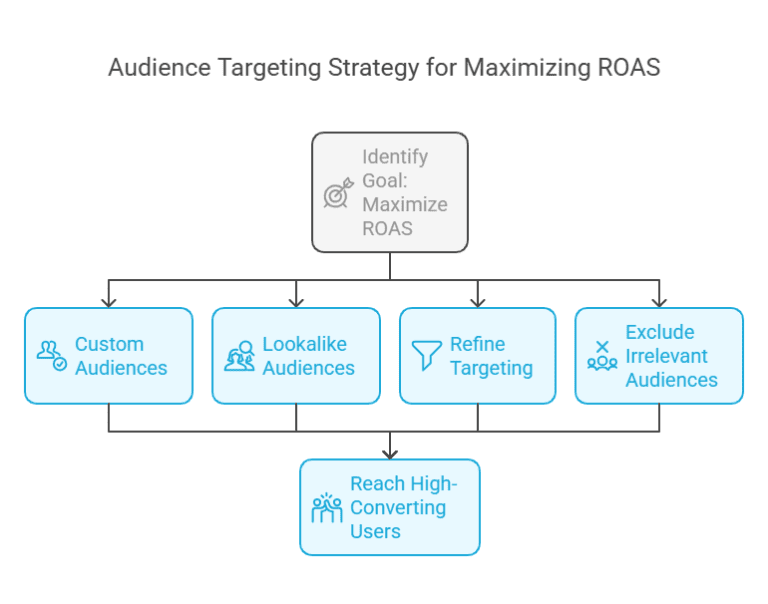
1. Audience Targeting
Reaching the right audience is essential for maximizing ROAS. Poor targeting leads to wasted ad spend on users who are unlikely to convert. Consider:
- Using custom audiences to target previous site visitors or engaged users.
- Leveraging lookalike audiences to find high-converting users based on existing customer data.
- Refining targeting based on demographics, interests, and behaviors to ensure you’re reaching the most relevant audience.
- Excluding irrelevant audiences to prevent wasting ad spend on users unlikely to convert.
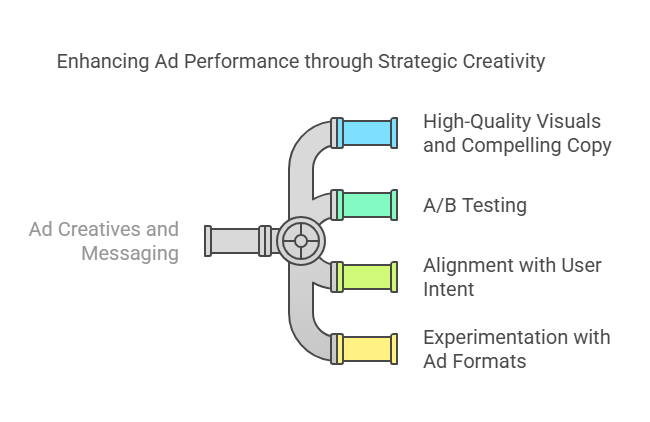
2. Ad Creatives and Messaging
Your ad’s design, copy, and call-to-action (CTA) directly impact engagement and conversions. To improve ROAS:
- Use high-quality visuals and compelling copy that resonate with your audience.
- A/B test different creatives to identify which designs, headlines, and CTAs drive the highest conversions.
- Align ad messaging with user intent and pain points, ensuring that the offer is relevant and attractive to your audience.
- Experiment with video ads, carousel ads, and interactive formats to increase engagement.
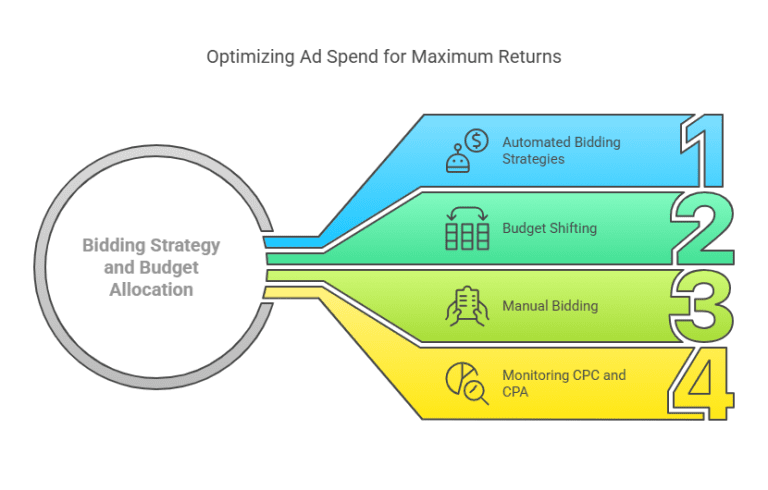
3. Bidding Strategy and Budget Allocation
How you allocate your ad budget plays a big role in return on ad spend. A few strategies to optimize bidding:
- Use automated bidding strategies (e.g., maximize conversions on Google Ads) to let AI adjust bids based on performance.
- Shift more budget to high-performing ads while cutting back on those with low engagement or conversion rates.
- Experiment with manual bidding if automated strategies are not delivering optimal results.
- Monitor cost-per-click (CPC) and cost-per-acquisition (CPA) to ensure that ad spend aligns with profitability.
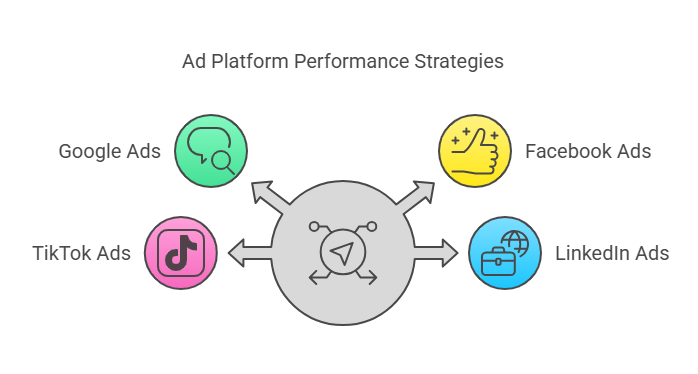
4. Ad Placement and Platform Performance
Not all platforms deliver the same ROAS. Google Ads, Facebook Ads, TikTok Ads, and LinkedIn Ads all perform differently depending on your audience and objectives.
- Test multiple platforms to identify where your audience engages most and which delivers the best ROAS.
- Optimize ad placement by removing low-performing ad placements, such as sites with low engagement rates.
- Adjust for device targeting (desktop vs. mobile) to ensure ads appear where users are most likely to convert.
- Consider native advertising and programmatic ad buying to reach audiences more effectively.
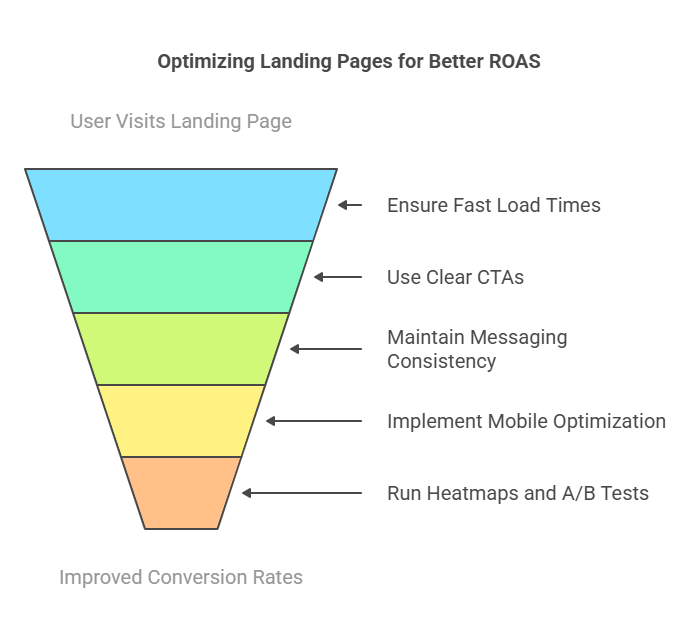
5. Landing Page Optimization
Even if your ad performs well, a poorly optimized landing page can hurt conversions, reducing ROAS. Best practices include:
- Ensuring fast load times (under 3 seconds) to prevent users from leaving due to delays.
- Using clear CTAs that guide users toward conversion, such as signing up, purchasing, or downloading content.
- Keeping messaging consistent between the ad and landing page to maintain user trust.
- Implementing mobile optimization, ensuring pages load properly on all devices.
- Running heatmaps and A/B tests to analyze how users interact with the page and improve conversion rates.
6. Seasonality and Market Trends
External factors like holiday shopping trends, economic conditions, and industry shifts can impact ROAS.
- Plan for higher ad costs during peak seasons, such as Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and holiday shopping periods.
- Use historical data to adjust budgets based on seasonal trends and anticipated traffic spikes.
- Leverage seasonal promotions and limited-time offers to capitalize on high consumer demand.
- Stay ahead of industry trends and changes in consumer behavior to adapt ad strategies proactively.
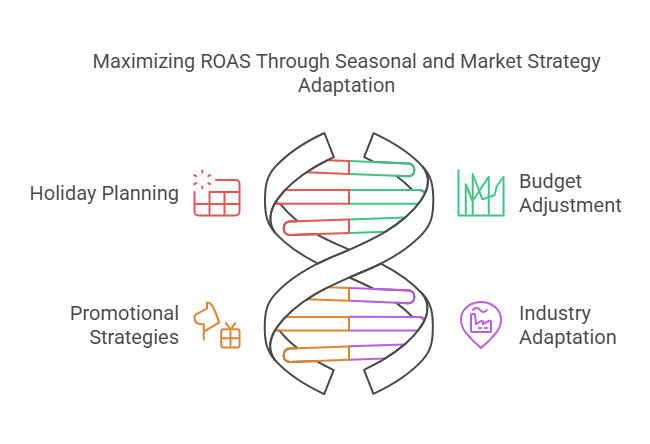
7. Competitor Activity
Competition affects ad costs and conversion rates. If multiple advertisers target the same audience, cost-per-click (CPC) rises, impacting ROAS.
- Monitor competitor ad strategies using tools like Facebook Ad Library and Google Ads Transparency Reports.
- Adjust bidding strategies based on competition levels to avoid overpaying for clicks.
- Differentiate your ads by highlighting unique selling points (USPs) and leveraging offers that competitors may not have.
- Consider using alternative advertising channels where competition is lower, such as niche platforms or influencer partnerships.

How to Improve Your Return on Ad Spend
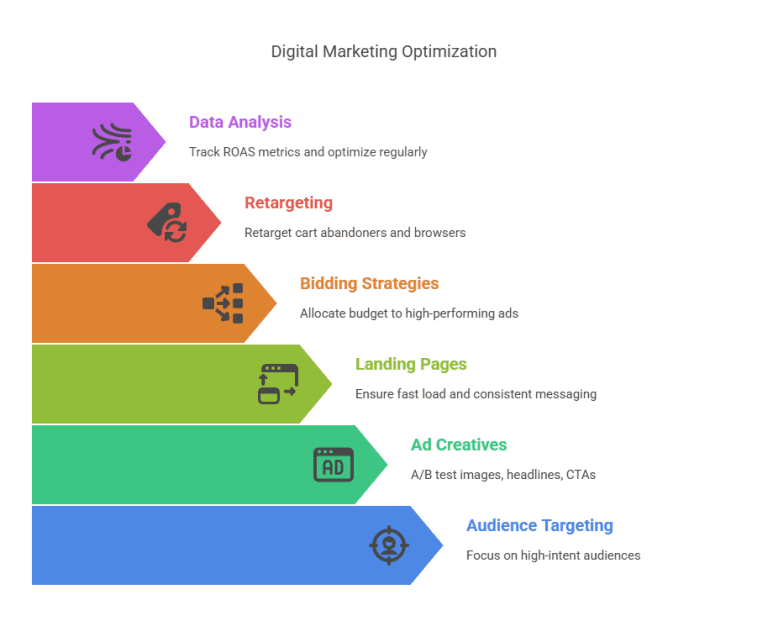
1. Refine Audience Targeting
- Focus on high-intent audiences (users who previously engaged with your brand).
- Exclude low-quality traffic sources to reduce wasted ad spend.
- Use behavior-based targeting to serve ads to users who have shown a high likelihood to convert.
2. Enhance Ad Creatives
- A/B test different images, headlines, and CTAs to optimize performance.
- Personalize ads for different audience segments to increase relevance.
- Use video and interactive ads to improve engagement and conversion rates.
3. Optimize Landing Pages
- Ensure pages load fast and have a strong conversion-focused layout.
- Match ad copy and landing page messaging for consistency.
- Use social proof, testimonials, and trust signals to boost credibility.
4. Adjust Bidding and Budgeting Strategies
- Allocate more budget to high-performing ads and keywords.
- Lower bids on keywords or placements with low conversion rates.
- Experiment with bid adjustments based on device, time of day, and audience demographics.
5. Leverage Retargeting Campaigns
- Retarget users who abandoned their cart or browsed without converting.
- Use dynamic retargeting to show users ads for specific products they viewed.
- Set up email follow-ups and cross-channel retargeting to re-engage potential buyers.
6. Analyze Data and Optimize Regularly
- Track key ROAS metrics using Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, or analytics tools.
- Identify which campaigns drive the highest ROAS and double down on them.
- Continuously test ad creatives, targeting, and placements to find the best combinations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a good ROAS?
A good ROAS varies by industry. Generally, a 4:1 ratio (earning $4 for every $1 spent) is considered profitable. However, businesses with lower margins may need a higher ROAS to stay profitable.
How does ROAS differ from ROI?
ROAS focuses only on ad spend vs. revenue, while ROI (Return on Investment) considers all costs, including production, overhead, and labor.
What happens if my ROAS is too low?
A low ROAS suggests that your ad campaigns aren’t generating enough revenue to justify the spend. To fix this, optimize targeting, creatives, landing pages, and bidding strategies.
Can a low ROAS still be profitable?
Yes, if your customer lifetime value (CLV) is high, a low ROAS might still lead to long-term profitability. Subscription-based and repeat purchase businesses often accept a lower ROAS upfront.
How do I track and analyze ROAS?
You can track ROAS using platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, or custom ROAS tracking spreadsheets.
Conclusion
Improving return on ad spend requires a mix of better audience targeting, stronger ad creatives, smart budget allocation, and continuous optimization.
By tracking the right data and making informed adjustments, businesses can maximize ad efficiency and profitability.
Want to measure your ROAS instantly? Use our ROAS Calculator to track your ad performance and make data-driven decisions today!
0 Comments