AI writing prompts help you guide a model toward the type of content you want. Instead of starting from a blank page, you give the system a clear goal, a format to follow, and the tone you need. This makes the writing process faster and more predictable, especially when you want structure or fresh variations.
People use AI prompts for many reasons. Some want support with ideas or outlines. Others want help revising drafts, exploring different styles, or creating content at a steady pace. A strong prompt acts like a set of instructions that shapes how the model responds.
This guide walks you through how AI prompts work, what makes them effective, and how to use them for better results. You will find practical examples, ready made templates, and a method you can apply across any writing task.
Key Takeaways
AI Writing Prompts
- AI writing prompts work by giving the model a clear goal and structure.
- Specific instructions produce more accurate and useful results.
- Strong prompts include context, format, tone, and boundaries to guide consistent output.
- Iteration improves output, since first responses are only starting points.
- Different tasks require different prompt styles, from short commands to detailed briefs.
- Effective prompting helps you create content faster and with greater consistency.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.
What are AI writing prompts
AI writing prompts are instructions you give a model so it can produce the type of content you need. These prompts tell the system what to create, how to structure it, and which tone or style to follow. Instead of offering a spark of imagination, they act as a practical guide that shapes the model’s behavior.
A prompt can be simple, such as asking for a short summary. It can also be detailed, with specific context, formatting rules, or constraints. The more clearly you explain your goal, the more reliable the output becomes. Good prompts reduce guesswork and help the model stay aligned with your intent.
AI tools continue to evolve, and prompt quality has a direct impact on the results they deliver as of this year. Clear direction remains the most effective way to improve accuracy and consistency.

How to write effective AI prompts
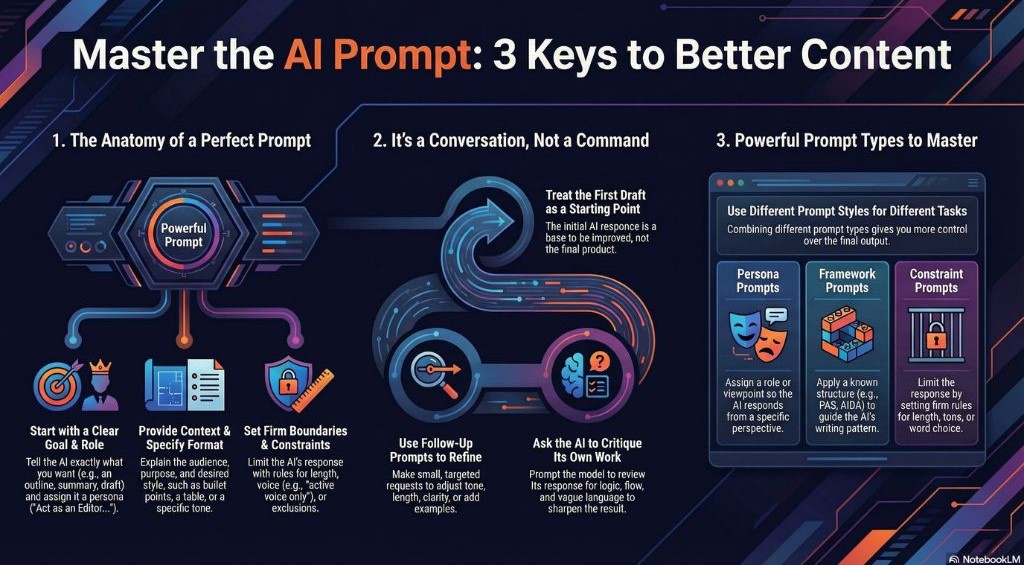
Effective AI prompts give the model enough direction to produce clear, useful results. Strong prompts combine purpose, structure, and a few guiding details. When you add context, formatting preferences, or role instructions, the output becomes more predictable and more aligned with your goals.
Give the model a clear goal
State exactly what you want, such as a summary, outline, draft, or comparison. Clear goals reduce guesswork. You can also assign a role to deepen focus, for example: “Act as an Editor in Chief and review this article for clarity and structure.” Persona prompts help the model choose a tone and point of view that supports your task.
Specify format, length, or style
Formatting instructions shape how the content appears. You may need bullet points, a short paragraph, a table, or a structured outline. Frameworks also guide style. For example: “Using the AIDA framework, write a short introduction for this product.” Format and structure give the model a path to follow.
Provide context or background
Context helps the model understand who the audience is, what the goal is, and why the content matters. Even a short detail can improve accuracy. You can also use simplifier or expert personas when you want content written for a specific reader group, such as: “Explain this concept as if you were teaching a beginner.”
Set boundaries or exclusions
Boundaries keep the model from drifting. You can limit tone, length, claims, or stylistic choices. Constraint patterns are useful here. For example: “Summarize this text in 120 words using only active voice.” Clear limits help the model stay focused.
Ask for revisions or refinements
Prompting is iterative. Use follow up instructions to adjust tone, tighten structure, or increase specificity. Refinement patterns can guide this process, such as: “Critique this paragraph for vague language, then rewrite it with concrete details.” Each revision moves the output closer to your intent.
Good prompts combine clarity, context, and structure. As you practice, you will learn when to add roles, when to choose a framework, and when to rely on constraints to guide the result. This blend creates more reliable and more consistent output across tasks.
🤖 Common types of AI writing prompts
AI prompts fall into a few broad categories that shape how the model interprets your instructions. These categories help you choose the right structure for your task, whether you are drafting new content, refining existing text, or experimenting with creative directions.
| Prompt type | What it does | Example use |
|---|---|---|
| Persona prompts | Assign a role or viewpoint to the model so it responds from a specific perspective. | “Act as an Editor in Chief and review this article for clarity and flow.” |
| Framework prompts | Apply a known structure to guide the model’s reasoning or writing pattern. | “Use the PAS framework to write a short product pitch for [AUDIENCE].” |
| Refinement prompts | Improve or revise text by adjusting tone, clarity, depth, or style. | “Critique this paragraph, then rewrite it in plain language.” |
| Constraint prompts | Limit how the model responds by setting rules for length, tone, or structure. | “Summarize this article in exactly 120 words using only active voice.” |
| Formatting prompts | Specify how the final output should appear, such as lists, tables, or structured outlines. | “Convert these notes into a checklist with clear action steps.” |
These types work individually or together. You can combine a persona, a framework, and a constraint in a single instruction when you want even more control. The clearer the structure, the more predictable the output becomes.
50 AI writing prompts
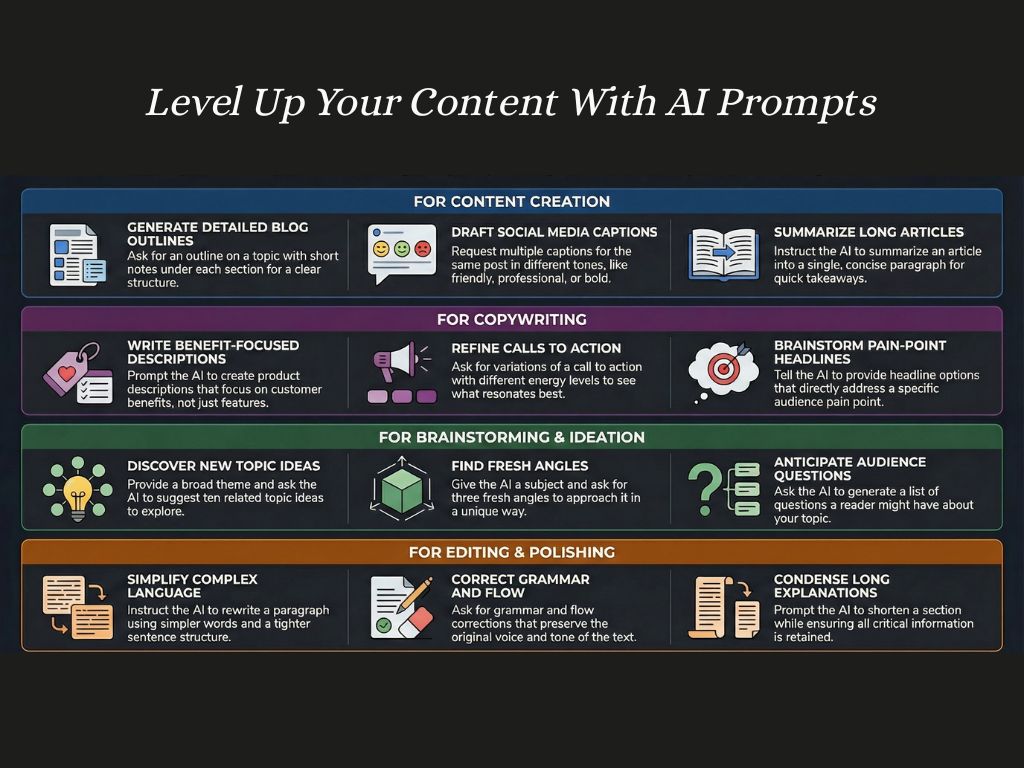
Below is a curated collection of prompts designed to cover the most common writing tasks creators face.
They’re organized by category, from Content Creation to Fiction, so you can quickly find the right prompt for the job.
How to use these prompts: Think of them as flexible templates. Copy and paste a prompt into your AI tool, then replace the placeholders (such as “this topic” or “this article”) with your specific details.
The clearer your input, the more useful and relevant the output will be.
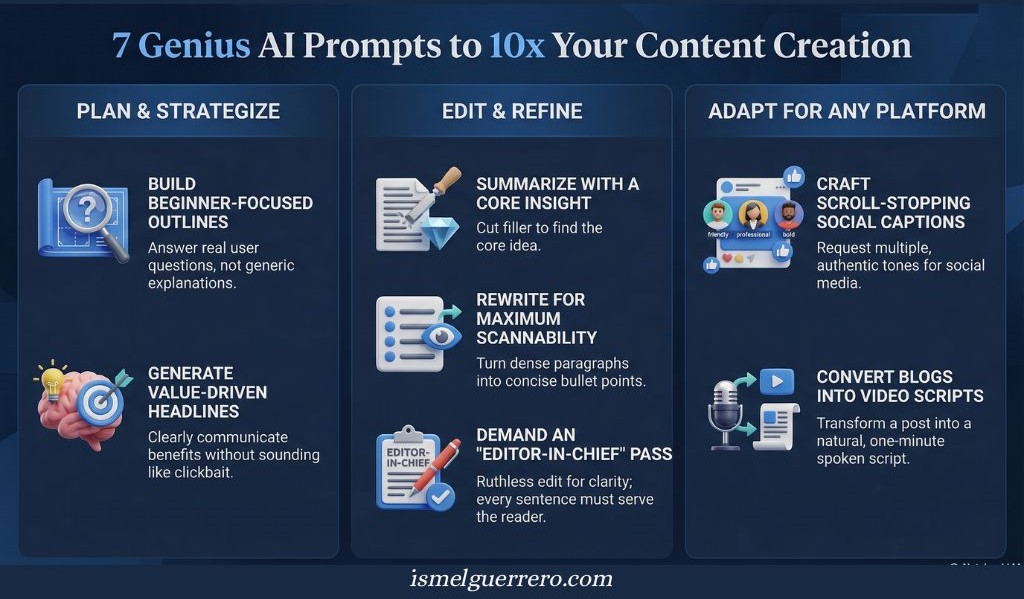
Content creation prompts
1. Beginner-Focused Blog Outline
Act as an experienced content creator. Create a clear blog outline for a beginner on this topic, with short notes under each section. Structure the outline around real questions and confusions beginners actually have, not textbook explanations. Replace any section that feels generic with a more practical, experience-based angle.
2. One-Paragraph Core Insight Summary
Act as a sharp editor. Summarize this article in one concise paragraph for readers who want the core idea fast. Focus only on what actually matters or changes the reader’s understanding. Cut background and filler.
3. Scroll-Stopping Social Captions
Act as a content creator who understands what stops the scroll. Create three social captions on this topic using different tones: friendly, professional, and bold. Each caption should sound like something a real person would post, not a brand or marketing template.
4. Concise, Scannable Rewrite
Act as an editor focused on clarity. Rewrite this paragraph into a concise, scannable version using bullet points. Remove repetition, filler, and abstract language while preserving the original meaning.
5. Editor-in-Chief Clarity Pass
Act as an Editor in Chief with strong reader judgment. Rewrite this section for clarity, flow, and reader focus. Every sentence must earn its place and directly serve the reader.
6. Value-Driven Headline Generator
Act as an editor, with strong taste for headlines. Suggest five headline ideas that communicate clear value without sounding promotional, clever, or click-driven. Avoid phrasing that feels commonly used.
7. One-Minute Video Script Conversion
Act as a creator experienced in short-form video. Convert this blog post into a natural, spoken script suitable for a one-minute video. Focus on one core idea and remove anything that feels like it is being read from a blog.

Copywriting prompts
8. Feature-to-Benefit Conversion (FAB)
Act as a direct-response copywriter. Turn this feature list into a benefits-driven paragraph that focuses on how the reader’s situation improves, not on the product itself. Avoid buzzwords and exaggerated claims.
9. Call-to-Action Optimization
Act as a copywriter with strong conversion instincts. Improve this call to action and provide three variations with different energy levels: calm and reassuring, confident and direct, and bold but grounded. Each version should feel natural, not salesy.
10. Reader-Centered Landing Page Rewrite
Act as a conversion-focused copywriter. Rewrite this landing page section so it speaks directly to the reader’s problem and desired outcome. Remove company-focused language and keep the attention on the reader.
11. Cold Email Introduction (AIDA-Inspired)
Act as an experienced email copywriter. Write an email that introduces this offer to cold subscribers using a simple attention → realization → relevance → next step flow. Keep it grounded, realistic, and free of hype.
12. Pain-Point Headline Generator
Act as an editor with strong audience awareness. Provide five headline options that speak directly to a specific audience pain point. Each headline should feel clear, human, and immediately relevant, not clever or vague.
13. Ad Concept Brainstorm (Problem → Outcome)
Act as a direct-response marketer. Generate three ad concepts that follow a simple problem-to-outcome flow. Focus on clarity and relatability rather than persuasion tricks or exaggerated promises.
14. Feature List to Plain-English Copy
Act as a copy editor who values simplicity. Rewrite this feature list into a single, easy-to-read paragraph that explains what the product does and why it matters, using plain language and concrete benefits.

Brainstorming and ideation prompts
15. Fresh Topic Idea Generator
Act as a creator who understands what audiences are tired of seeing. Suggest ten topic ideas based on this theme that avoid the usual surface-level talking points. Prioritize specificity and relevance over broad appeal.
16. Non-Obvious Content Angles
Act as a strategist with strong creative judgment. Offer three distinct angles for an article or piece of content on this subject that approach it from a less-discussed perspective. Replace any angle that feels commonly repeated online.
17. Content Series Builder
Act as an experienced content planner. Create a list of potential subtopics that could support a cohesive content series around this theme. Each subtopic should logically build on the previous one without overlapping.
18. Brand-Aligned Naming Ideas
Act as a brand strategist with strong naming instincts. Generate naming ideas that match this brand’s tone and personality. Avoid trendy buzzwords or names that feel generic or forced.
19. Unexpected Concept Combiner
Act as a creative thinker. Provide five content concepts that combine two seemingly unrelated themes in a way that feels natural and interesting, not gimmicky.
20. Audience Question Discovery
Act as someone who understands audience curiosity. Suggest questions a reader or viewer might realistically ask about this topic, focusing on confusion, doubt, or decision-making moments rather than basic definitions.
21. Idea Variation Generator
Act as a creator exploring different depths of the same idea. Offer ten variations of this core idea, ranging from simple and introductory to more nuanced and advanced, without repeating the same angle.
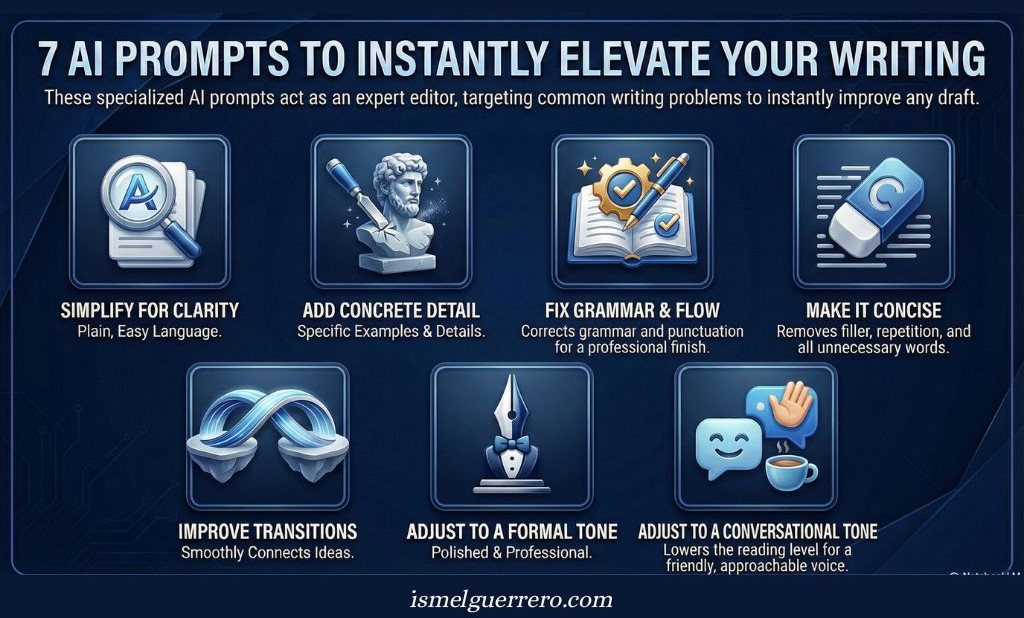
Editing and polishing prompts
22. Plain-Language Rewrite
Act as an editor who values clarity over complexity. Rewrite this paragraph using simpler language and tighter structure while preserving the original meaning and voice.
23. More X, Less Y Refinement
Act as a skilled editor. Rewrite this paragraph with more concrete examples and specificity, and less abstraction or vague phrasing. Keep the message intact while making it easier to grasp.
24. Grammar and Flow Cleanup
Act as a professional copy editor. Fix grammar, punctuation, and flow issues in this text without changing the tone or voice.
25. Concise Explanation Edit
Act as an editor focused on efficiency. Shorten this explanation while keeping every important idea. Remove repetition, filler, and unnecessary qualifiers.
26. Transition Improvement
Act as a developmental editor. Improve the transitions between these two paragraphs so the ideas connect smoothly and logically without adding new content.
27. Formal Tone Adjustment
Act as an editor adjusting for audience expectations. Raise the reading level so the text sounds more formal and polished, without making it stiff or academic.
28. Conversational Tone Adjustment
Act as an editor focused on readability. Lower the reading level so the text feels more conversational and approachable, without sounding casual or sloppy.

Research and analysis prompts
29. Tool Comparison Breakdown
Act as a neutral analyst. Compare these two tools and list the meaningful differences that would actually affect a real user’s decision. Focus on practical trade-offs, not feature lists.
30. Balanced Argument Summary
Act as a clear-minded researcher. Summarize the main arguments on both sides of this issue in plain language. Present each side fairly without trying to persuade or conclude.
31. Pattern Identification
Act as an analyst looking for signals, not noise. Identify patterns in this data and explain what they suggest in simple, concrete terms without speculation or jargon.
32. Complex Topic Deconstruction
Act as a subject-matter explainer. Break this complex topic into smaller, understandable concepts with short definitions that build clarity instead of overwhelm.
33. Insight Extraction
Act as a researcher with strong judgment. Extract five insights from this source that are not immediately obvious and explain why each one matters.
34. Beginner-Friendly Research Overview
Act as an experienced educator. Turn this research document into a clear overview for beginners, focusing on what they need to understand first and why.
35. Risk and Consideration Analysis
Act as a cautious decision-maker. List potential risks, downsides, or considerations related to this decision, prioritizing realistic concerns over edge cases.

Fiction and storytelling prompts
36. Character Profile Builder
Act as a storyteller focused on believable characters. Develop a character profile that includes clear goals, core fears, internal conflicts, and defining traits. Prioritize psychological depth over surface description.
37. Three-Act Story Outline
Act as a narrative strategist. Outline a three-act story structure based on this idea, ensuring each act creates momentum and meaningful change for the main character.
38. Scene Rewrite for Tension
Act as a fiction editor. Rewrite this scene to increase tension and sensory detail, focusing on what the character notices, feels, and avoids rather than explaining emotions directly.
39. Tone-Aligned Plot Twists
Act as a story consultant. Suggest plot twists that fit the established tone and themes of this story. Avoid twists that feel random or purely for shock value.
40. Conflict Expansion
Act as a developmental editor. Expand this character conflict into a concise scene summary that clearly shows what’s at stake and why the conflict matters now.
41. Emotion-Driven Setting Description
Act as a visual storyteller. Describe a setting that reflects the character’s emotional state, using concrete details and atmosphere instead of abstract description.
42. Genre-Specific Rewrite
Act as a genre specialist. Rewrite this scene using the conventions of the specified genre while preserving the core characters, conflict, and intent of the original scene.

Productivity and workflow prompts
43. Goal-to-Execution Breakdown
Act as a practical productivity strategist. Turn this goal into a clear, realistic plan that focuses on progress, not perfection, and avoids unnecessary complexity.
44. Task Decomposition
Act as an operations-minded planner. Break this large task into smaller, concrete actions that feel manageable and logically sequenced.
45. Weekly Workflow Builder
Act as a workflow designer. Create a simple weekly workflow that supports this project without overloading any single day.
46. Process Simplification Audit
Act as an efficiency consultant. Suggest ways to streamline this process while preserving quality and reducing friction.
47. Meeting-to-Action Translator
Act as an execution-focused assistant. Turn this meeting transcript or notes into a clear, prioritized list of actionable next steps.
48. Structured Project Outline
Act as a project organizer. Rewrite these notes into a clean, structured project outline that makes the scope and priorities obvious.
49. Completion Checklist Creator
Act as a systems thinker. Create a concise checklist for completing this task from start to finish, focusing only on what actually moves it forward.
50. Sustainable Routine Designer
Act as a productivity coach. Design a daily or weekly routine that fits the user’s real schedule and energy levels, not an idealized version of productivity.
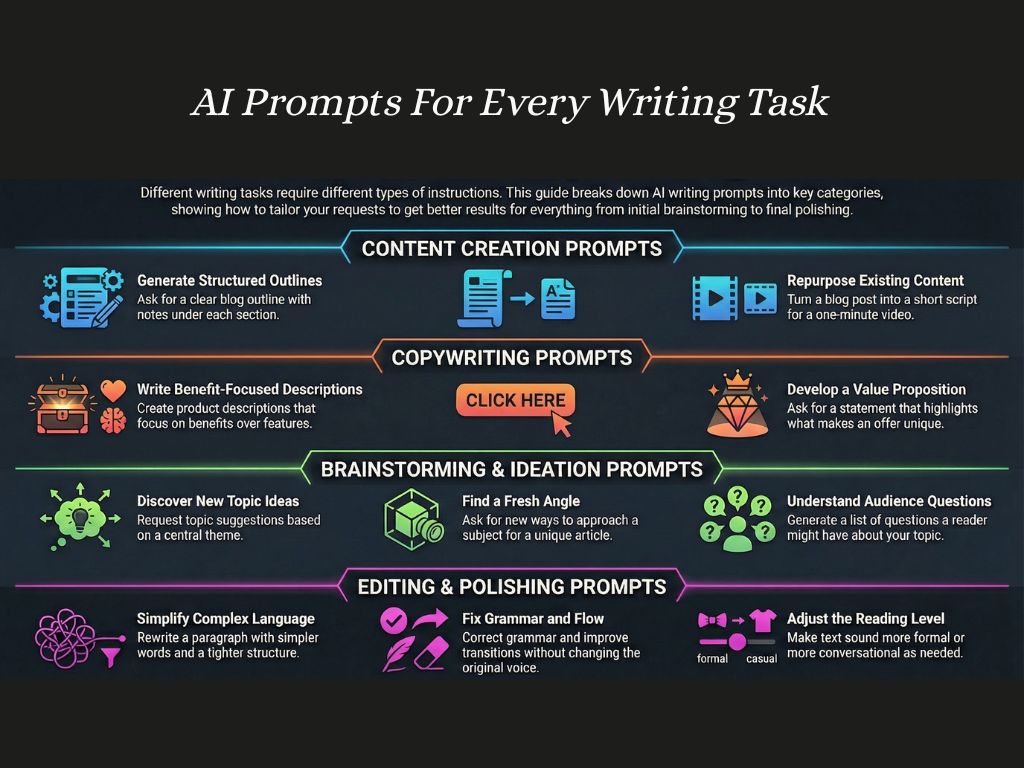
How to choose the right AI prompt for your task
AI prompts work best when they match the type of output you need. A short command may be enough for a summary, but a detailed brief is more useful when you want structure, tone, or specific examples. The goal is to align the complexity of your prompt with the complexity of the task.
Start by identifying the purpose. Are you trying to brainstorm, draft, refine, or analyze something? Each purpose benefits from a different level of detail. Simple tasks need concise instructions. Complex tasks need context, boundaries, and clear expectations.
Consider your audience as well. A prompt written for technical readers will guide the model differently than one aimed at beginners. When you include audience details, the output becomes more precise and more relevant.
You can adjust depth based on how much control you want. If you want flexibility, keep the prompt open. If you want consistency, add more structure. As a general rule, clarity always improves results, and small adjustments often make a noticeable difference.
A brief credibility note fits here: AI tools continue to refine how they interpret instructions, so prompt design remains one of the most reliable ways to influence output as of this year.

How to refine AI output with follow up prompts
First drafts from an AI model are starting points. The strength of the final result often depends on how you refine it. Follow up prompts help you adjust tone, structure, clarity, and depth without rewriting the entire instruction. Small, targeted requests guide the model toward a version that fits your needs more closely.
Request a different tone
Ask the model to shift the voice toward a specific mood, such as formal, friendly, neutral, or direct. Tone changes can transform how the content feels without altering the message.
Adjust length or depth
If the response feels too short, ask for expansion with examples or added context. If it feels too long, request a concise version. Length control improves readability and focus.
Ask for more examples
Examples help clarify complex ideas and make content easier to apply. You can request lists, scenarios, or alternative approaches to widen your options.
Clarify missing details
If something feels vague, ask the model to explain the reasoning, define key terms, or fill gaps. This reduces ambiguity and strengthens accuracy.
Improve accuracy or coherence
When details seem inconsistent or unclear, ask the model to review its own output for logic, flow, or factual alignment. A self check prompt often sharpens the response.
Iteration is a natural part of working with AI. Each adjustment brings the output closer to your goal and helps you understand which types of prompts work best for your tasks.

Common mistakes with AI prompts and how to avoid them
AI prompts can feel straightforward, but small gaps in direction often lead to unclear or unfocused results. Understanding the most common mistakes helps you shape instructions that produce stronger, more reliable output.
Vague goals
A prompt that asks for “content on this topic” leaves too much room for interpretation. Define what you want, such as an outline, a summary, or a draft. Clear goals prevent confusing results.
Missing context
When a prompt lacks audience, purpose, or background information, the model fills those gaps on its own. Adding even a short description improves alignment and accuracy.
Contradicting instructions
Asking for a short answer and a detailed explanation at the same time creates mixed signals. Choose one direction. If you need both, separate them into two steps.
Overloading the prompt
Long, dense instructions can overwhelm the model. Break complex requests into smaller parts, or handle them with follow up prompts.
Skipping revision
Many users treat the first response as final. Iteration helps refine tone, structure, clarity, and depth. A brief follow up prompt often improves the output significantly.
Avoiding these mistakes makes prompting more consistent and helps the model produce the kind of content you can use with minimal editing.
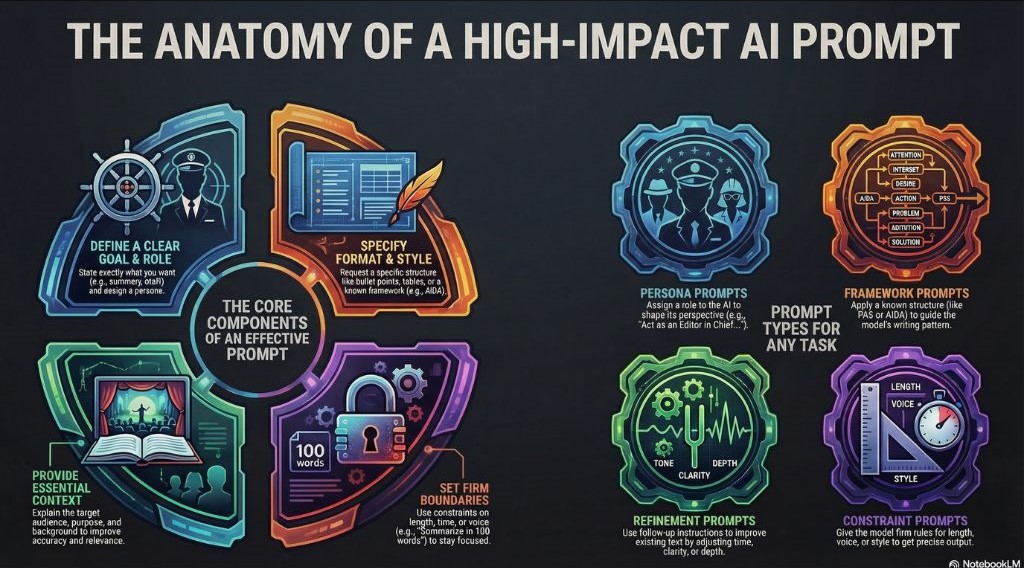
Explore more AI prompt ideas
AI prompts can support a wide range of tasks, from content creation to creative exploration. Once you understand how basic prompts work, you can use more advanced structures to guide tone, refine drafts, or create specialized outputs. The ideas below give you a practical way to expand your prompting skills.
Persona prompts for stronger alignment
Persona prompts shape the model’s point of view. They help you create more targeted content and more realistic feedback.
- Expert Persona Prompt. Ask the model to adopt the voice and judgment of a professional in a specific field.
- Audience Persona Prompt. Request feedback from a fictional customer or reader to uncover objections.
- Simplifier Persona. Tell the model to explain a complex topic as if teaching a beginner.
- Editor in Chief Prompt. Ask the model to review a draft for structure, clarity, and strength of argument.
These prompts are useful when tone, perspective, or expertise influence the final result.
Framework prompts for structured thinking
Framework prompts guide the model by giving it a proven writing or marketing structure to follow.
- PAS framework. Generate copy that moves from problem to agitation to solution.
- AIDA structure. Write content that follows attention, interest, desire, and action.
- FAB expansion. Turn a feature list into advantages and benefits.
- StoryBrand pattern. Position the user as the hero and the product as the guide.
Frameworks help you shape content that flows logically and remains consistent.
Refinement prompts for improving drafts
Refinement prompts build on text you already have. They help you improve clarity, accuracy, tone, and usefulness.
- Critique and Rewrite. Ask the model to evaluate weaknesses before rewriting.
- More X Less Y refinement. Increase one quality while reducing another.
- Eliminate Jargon. Convert technical writing into plain language.
- Add Emotional Hook. Strengthen the opening of a paragraph with a clearer emotional focus.
These prompts help you polish content without losing your original voice.
Constraint prompts for focused output
Constraint prompts give the model firm rules. They act as guardrails that keep the output consistent and easy to format.
- Word limit constraint. Ask for a specific word count.
- No passive voice. Request active voice throughout.
- First person only. Maintain a single perspective.
- Single paragraph constraint. Summarize a long text into one cohesive block.
Constraints help when you need precision, such as social copy, summaries, or platform specific content.
Formatting prompts for clean presentation
Formatting prompts tell the model how to present information rather than how to write it.
- Markdown table format. Turn research notes into a structured table.
- Checklist output. Convert steps into a clear list of action items.
- Slide style format. Break content into short slide style sections.
- Comparative matrix. Compare products or ideas across multiple criteria.
These prompts are ideal for planning, organization, and documentation.

Conclusion
AI writing prompts help you work with more clarity and less guesswork. A good prompt sets direction, provides structure, and gives the model the context it needs to produce useful results. Once you learn how to shape your instructions, the output becomes easier to guide and easier to refine.
The prompts and frameworks in this guide offer a starting point for many types of writing tasks. You can use them to draft content, plan ideas, revise language, or explore creative concepts. Each prompt is flexible, and each can be adjusted to match your goals.
Strong prompting is a skill that improves through practice. The more you experiment, the more you understand how small changes influence the response. Over time, you will develop a set of instructions that consistently deliver the tone, depth, and structure you want.
AI tools evolve quickly, but clarity and thoughtful iteration remain the foundation of reliable results. With the right prompts, you can shape the writing process with confidence and keep your workflow steady.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is an AI writing prompt
An AI writing prompt is an instruction that tells a model what to create, how to shape the content, and which tone or format to follow. It acts as a guide rather than a story starter. Clear prompts help the system produce more accurate and useful results.
How specific should an AI prompt be
Specific prompts often produce better outputs because they reduce guesswork. You can define purpose, audience, tone, and structure without making the instruction overly complex. If the task needs depth, add detail; if it is simple, keep the prompt short.
Why does the first AI response sometimes miss the mark
First drafts are broad attempts to meet your request. They may lack context or detail. Follow up prompts help correct direction, refine clarity, and bring the output closer to your intent.
Can AI prompts improve content quality
They can improve clarity, structure, and efficiency. Strong prompts give the model a pattern to follow, which helps the final draft feel more focused. You still guide tone and accuracy through iteration.
Do different AI tools require different prompting styles
Most principles stay consistent across tools, such as clear goals and helpful context. Some systems respond better to short commands while others handle detailed briefs well. A small amount of testing usually shows which style works best.
How do I fix unclear or unfocused AI responses
Add more context, specify the format you want, or request a revision with clearer boundaries. You can also ask the model to identify which parts of your prompt were unclear. Refinement usually improves the result.
What tasks are best suited for AI prompts
AI prompts support many tasks, such as drafting content, writing outlines, brainstorming ideas, refining language, or analyzing information. They are most effective when the goal is clear and the structure can be described in advance.
- AI Side Hustles Guide.
- High-Paying Writing Side Hustles.
- Easy Side Hustles You Can Start Today.
- AI Side Hustle Ideas.
- Best Prompt Generator.
- Creative Writing Prompts.
- Text-to-Image AI Explained.
- The ERA Framework.
- The CREATE framework.
- AI Prompt Examples That Actually Work.
- CARE Prompt Framework.
- Multi-Chain Prompting.
0 Comments