Introduction
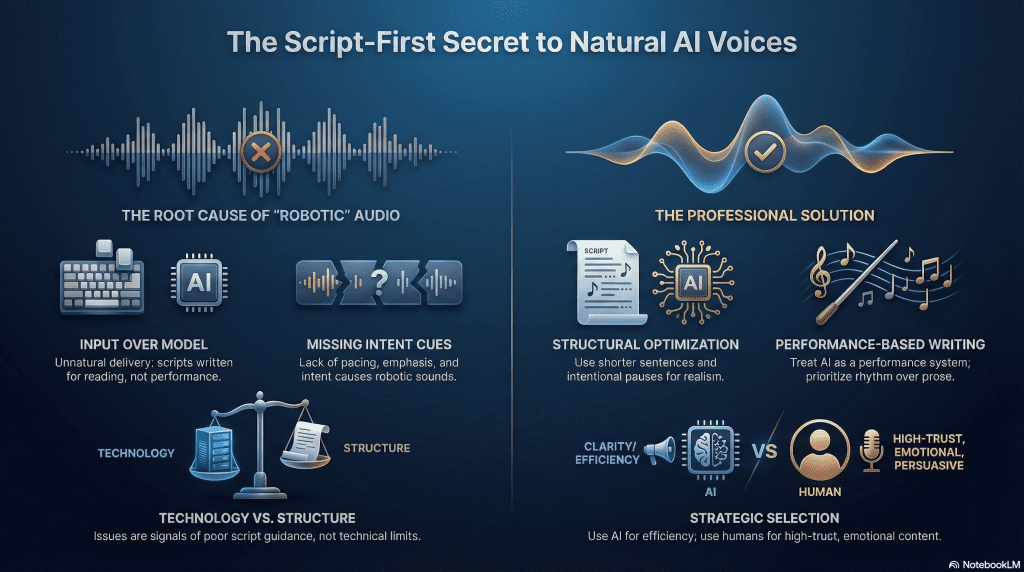
AI voice overs often sound unnatural for a simple reason, they are generated from scripts that were never written to be spoken. Listeners notice flat tone, awkward pacing, or misplaced emphasis, even when the voice itself is technically advanced.
This is not a model problem, it is an input problem rooted in how the text is structured and guided. When scripts lack rhythm, intent, and clear delivery cues, the audio exposes those gaps immediately.
This article explains why AI voice overs feel unnatural and shows how to fix the underlying issues before changing tools or voices.
Key Takeaways
- AI voice overs sound unnatural most often because scripts are written for reading, not speaking.
- Long, dense sentences force the AI to guess pacing and emphasis, which leads to flat or awkward delivery.
- Script structure directly controls how an AI voice handles timing, pauses, and meaning.
- Shorter sentences and intentional breaks improve voice quality without changing tools or models.
- Clear intent in the text matters more than voice selection or emotional instructions.
- Most AI voice problems are fixed at the script level, before audio is ever generated.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.

What people mean when they say AI voice sounds unnatural
When listeners describe an AI voice as unnatural, they are usually reacting to delivery, not pronunciation. The words may be correct, but the timing feels off. Pauses appear in the wrong places, emphasis lands on unimportant words, and sentences run together without breathing room.
Another common complaint is emotional flatness. The voice does not sound robotic in a mechanical sense, but it lacks intention. Important points do not feel important, and transitions do not signal shifts in meaning. This creates a sense that the voice is reading text rather than communicating an idea.
These issues are easy to misdiagnose as limitations of the voice model. In practice, they are signals that the script did not give the AI enough guidance. When intent, rhythm, and structure are unclear in the text, the audio makes that absence obvious to the listener.
The real reasons AI voice overs sound wrong
Most AI voice overs sound wrong because the script is doing too much work at once. Ideas are packed into long sentences, clauses pile up, and the text assumes the voice will know where to slow down or emphasize meaning. Spoken language does not work that way. When the script is dense, the delivery becomes rushed or uneven.
Another issue is the absence of intent cues. Scripts often state information without signaling why it matters or how it should feel. Without guidance on tone, contrast, or priority, the AI delivers everything at the same level. This flattens the audio and makes important points blend into background noise.
Finally, many scripts are written as finished prose instead of performance text. They look good on the page but fail when spoken aloud. AI voice systems can only work with what they are given. If the text does not account for pacing, emphasis, and flow, the output will reflect those limitations exactly.
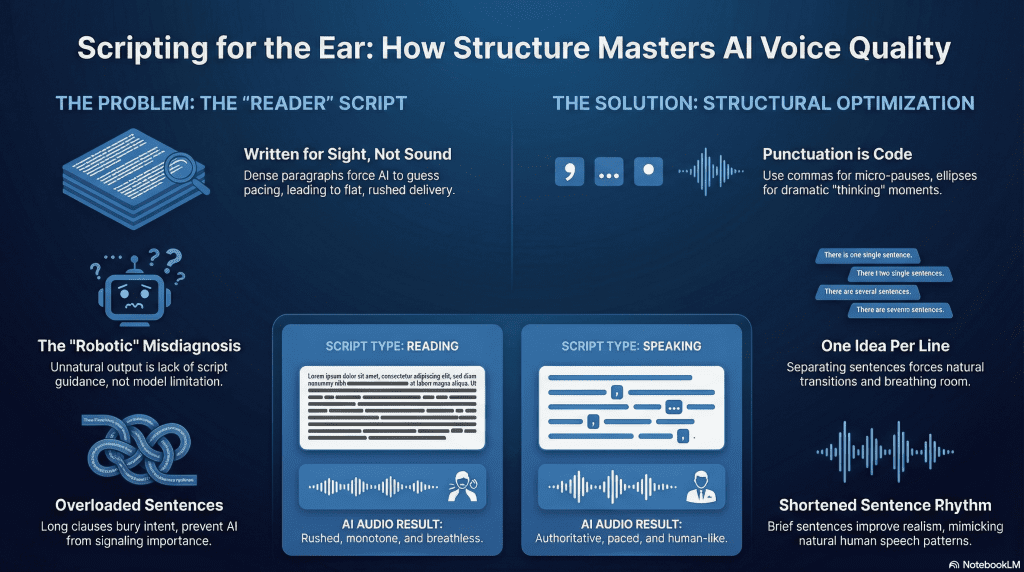
How script structure affects AI voice quality
Script structure determines how an AI voice interprets timing, emphasis, and flow. When sentences are short and purposeful, the voice naturally sounds more deliberate. When sentences are long and layered, the delivery becomes strained because the AI has no clear signal for where meaning shifts.
Written text often relies on punctuation and visual spacing to guide understanding. Spoken audio relies on rhythm and breath. Scripts that ignore this difference force the AI to guess where pauses belong, which leads to awkward pacing or unnatural stress on words that do not deserve it.
Clear structure solves this. Breaking ideas into smaller units, using intentional line breaks, and separating key points gives the AI room to breathe. The voice sounds more natural not because the technology improved, but because the script finally reflects how people speak rather than how they read.
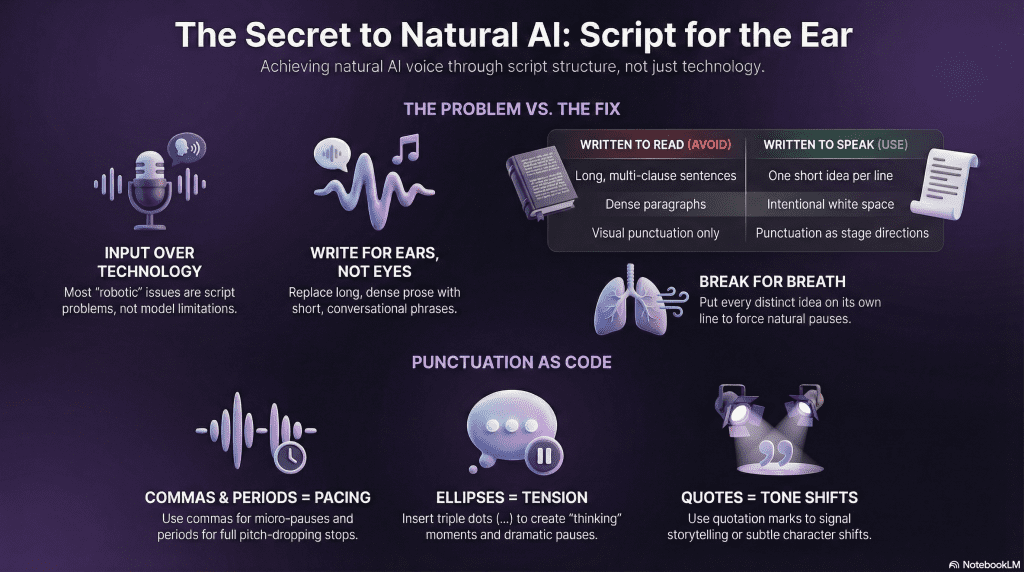
⚡ Pro Tip: Punctuation is Code
AI models treat punctuation as “stage directions” for breathing and timing. Use them intentionally:
- Commas ( , ) = A micro-pause. Use these to group ideas.
- Periods ( . ) = A full stop. The AI will drop its pitch and take a “breath.”
- Ellipses ( … ) = A dramatic pause. Use this to create tension or a “thinking” moment.
- Quotation Marks ( ” ” ) = A tone shift. The AI often subtly changes its voice to sound like it is telling a story.

Before vs After: How Script Structure Changes AI Voice Delivery
Before (written to be read, not spoken):
AI voice overs are becoming more popular across content platforms because they offer efficiency and scalability, but many creators struggle with unnatural delivery that can reduce listener engagement and trust.
Why it sounds unnatural:
- Sentence is too long
- Multiple ideas compete for emphasis
- No clear pacing or vocal priority
- The AI treats everything as equally important
After (written to be spoken):
AI voice overs are becoming more popular.
They’re fast. They scale easily.
But many creators still struggle with one problem.
The delivery sounds unnatural. And when that happens, listeners lose trust.
Why this sounds more natural:
- Each idea has its own space
- Natural pauses are built into the structure
- Emphasis is implied through sentence length, not instructions
- The AI doesn’t have to guess where meaning shifts
Key takeaway: The voice didn’t improve because the model changed. It improved because the script finally matched how people speak.

How to guide AI voice delivery more precisely
Guiding AI voice delivery starts with making intent visible in the script. The voice cannot infer what matters most unless the text signals it. Simple techniques, such as separating key points onto their own lines or shortening sentences that carry emphasis, help the AI prioritize meaning.
Pacing is another control point. Long paragraphs encourage rushed delivery, while intentional breaks slow the voice down naturally. Dividing the script into short, spoken units gives the AI clear places to pause without needing technical markers or complex instructions.
Tone also benefits from clarity rather than adjectives. Instead of asking for an emotional style in abstract terms, shape the tone through word choice and sentence structure. When the script reads the way a person would speak, the AI voice follows that lead with fewer errors and more natural flow.
💡 The Script Clinic: Before vs. After
See how a small change in structure changes the audio output.
❌ The “Reader” Script (Bad) “Welcome to the course, today we are going to learn about three marketing strategies that will help you grow your business faster and more efficiently than ever before.”
- Result: The AI rushes through the sentence in one breath. It sounds like a generic disclaimer at the end of a commercial.
✅ The “Speaker” Script (Good) “Welcome to the course.
Today, we are going to learn three specific marketing strategies.
These strategies will help you grow your business faster… and more efficiently than ever before.”
- Result: The AI pauses naturally at the line breaks. It emphasizes “faster” because of the ellipsis. It sounds authoritative and human.
Common mistakes that make AI voice worse
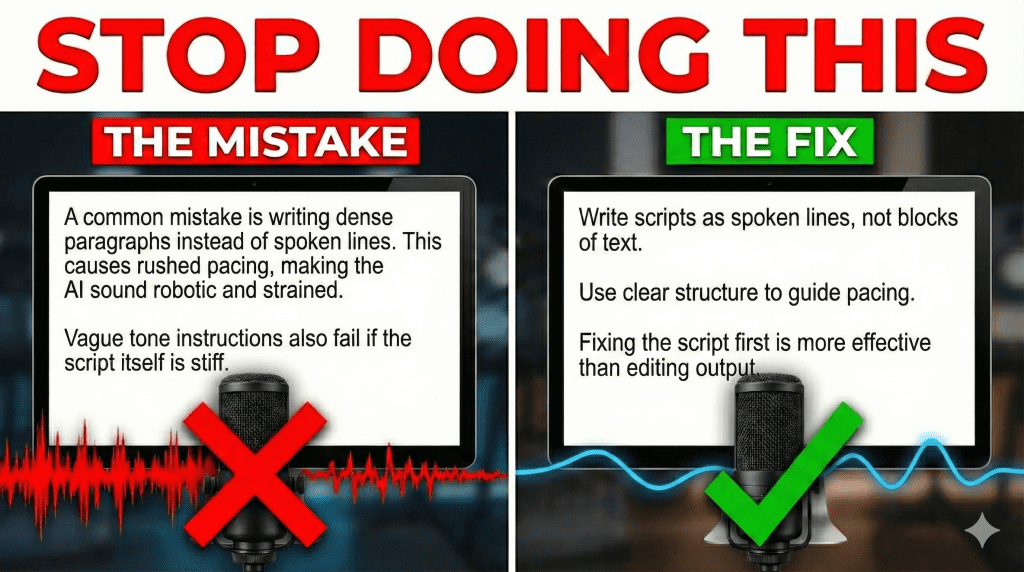
One common mistake is writing scripts as dense paragraphs instead of spoken lines. When too much information is packed into a single block of text, the AI delivers it without natural pauses. This causes rushed pacing and makes even a high-quality voice sound strained.
Another issue is relying on vague tone instructions instead of structural guidance. Telling an AI to sound friendly or engaging does little if the script itself is stiff or overloaded. Tone emerges from sentence length, word choice, and emphasis, not from labels added at the end of a prompt.
Many people also try to fix voice problems after generation instead of before. Editing audio output is slower and less effective than fixing the script. When the input text is clear, paced, and intentional, the AI voice improves automatically without additional processing.
When AI voice over is the wrong choice
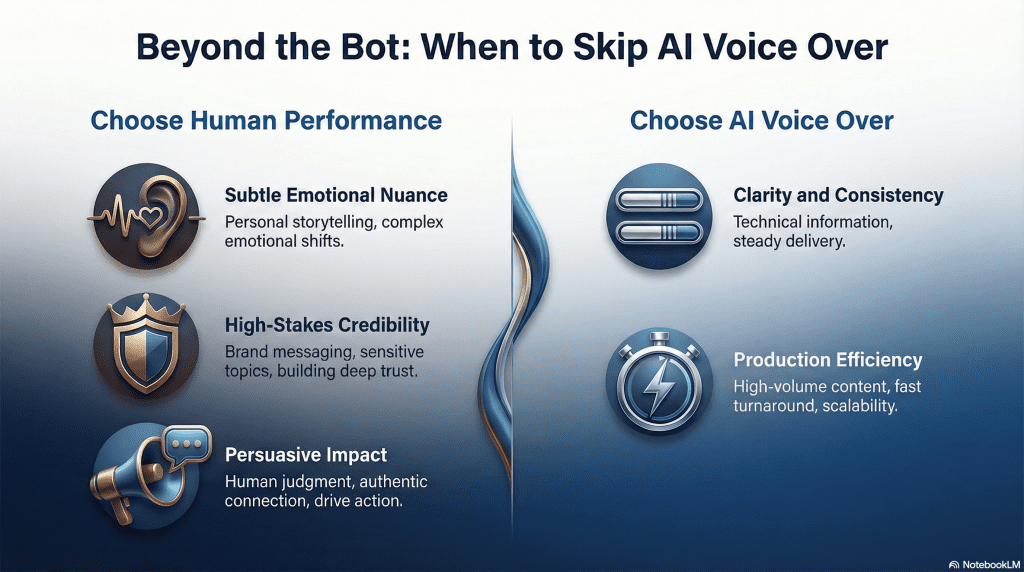
AI voice over is not always the best option, even when the script is well written. Content that depends on subtle emotional shifts, personal storytelling, or persuasion often requires human judgment in delivery. In these cases, the limitations are not technical, they are expressive.
High-stakes situations also favor human voices. Brand messaging, sensitive topics, or material where trust is critical can suffer if the voice feels even slightly off. Listeners are quick to notice when tone does not match context, and small mismatches can undermine credibility.
AI voice works best when clarity and consistency matter more than emotional nuance. Knowing when not to use it is part of producing better audio overall. Choosing the right medium protects the message, not just the efficiency of production.
Bonus: The “Voice Over Formatter” Prompt
You don’t always have to manually edit every line. If you are starting with a blog post or a dense document, you can use an LLM (like ChatGPT or Claude) to do the heavy lifting for you.
Use this prompt to instantly convert “Reading Text” into “Speaking Text” that is ready for your AI voice tool.
copy-paste this prompt:
“Act as a professional Voice Over Scriptwriter. I am going to give you a text that was written for reading. I need you to rewrite it for spoken audio delivery.
Follow these formatting rules strictly:
- Format: Break every distinct idea onto its own new line. Do not use paragraphs.
- Pacing: Use ellipses (…) to indicate natural thinking pauses or transitions.
- Simplification: Shorten long sentences. Remove filler words.
- Tone: Make it conversational and direct, as if speaking to a friend.
- Punctuation: Use commas frequently to force small micro-pauses.
Here is the text to rewrite: [Insert your text here]”

Conclusion
AI voice overs sound unnatural far more often because of script and structure issues than because of the technology itself. When text is written to be read instead of spoken, the voice exposes every weakness in pacing, emphasis, and intent. Fixing those problems at the input level produces more natural results than switching tools or voices.
The key is to treat AI voice as a performance system, not a reading machine. Clear structure, intentional phrasing, and realistic pacing give the voice what it needs to sound human. When those elements are in place, AI voice over becomes a practical and effective option rather than a compromise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do AI voice overs sound robotic even with good voices?
Most robotic-sounding output comes from scripts that lack pacing, emphasis, or clear intent. Even high-quality voices struggle when the input text is dense or written for reading instead of speaking.
Can rewriting the script really improve AI voice quality?
Yes. Script changes often have a bigger impact than changing the voice model. Shorter sentences, clearer structure, and intentional pauses help the AI deliver more natural audio.
Is unnatural AI voice a limitation of the technology?
Sometimes, but not usually. In most cases, the issue is incomplete or poorly structured input. The technology follows the text it is given very closely.
When should I choose a human voice over instead of AI?
Human voice over is better for emotionally nuanced, persuasive, or high-trust content. AI voice works best when clarity, consistency, and efficiency are the priorities.
0 Comments