Introduction
User-generated content (UGC) is one of the most common types of content on the internet today, yet many people don’t clearly understand what it actually means.
Every time someone posts a video, writes a review, shares a tutorial, or comments on a product, they are creating UGC. This type of content matters because it influences opinions, trends, and buying decisions far more than traditional advertising.
As social platforms continue to reward authenticity over polish, UGC has become central to how content spreads and creates value online.
This guide explains exactly what UGC is, how it works, and why it has become so important.
Key Takeaways
- User-generated content (UGC) is content created by real people, not brands or companies.
- UGC includes videos, photos, reviews, posts, comments, and tutorials shared online.
- The value of UGC comes from authenticity, not production quality or follower count.
- UGC is popular because people trust personal experiences more than polished messaging.
- Anyone can create UGC, casually or intentionally, without special tools or credentials.
- UGC is a content type, not a job, but it can lead to opportunities over time.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.

What Is User-Generated Content (UGC)?
User-generated content (UGC) is any content created by people rather than brands or companies. It includes videos, photos, reviews, comments, posts, tutorials, and other media shared online based on personal experience or opinion.
What defines UGC is who creates it, not where it appears or how polished it looks. If the content comes from a real person speaking in their own voice, it qualifies as UGC. This is true whether the content is shared casually or created with intention.
UGC is different from brand-created content because it is typically less scripted and less tightly controlled than company-produced content. It reflects how people naturally communicate, which is why it often feels more relatable and can build trust with audiences.
Today, UGC is a major force behind how information spreads online. It shapes trends, influences decisions, and plays a central role across social media, communities, and digital platforms.
Why User-Generated Content Is So Popular
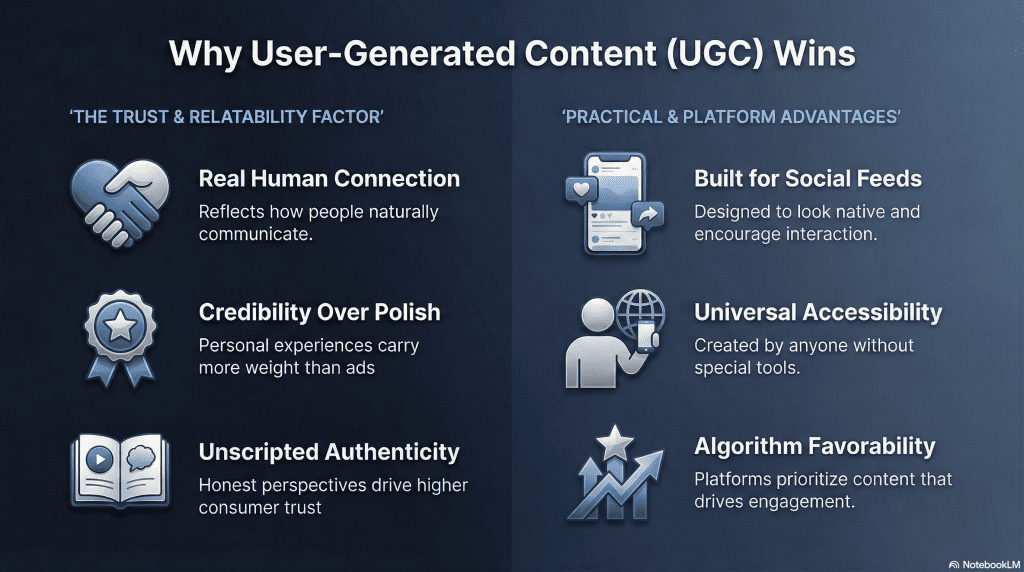
User-generated content is popular because it reflects how people actually communicate online. Instead of polished messages designed to persuade, UGC feels natural, personal, and familiar. People recognize themselves in it, which makes it easier to trust and engage with.
Another major reason is credibility. When content comes from real individuals sharing opinions or experiences, it carries more weight than traditional advertising. Reviews, tutorials, and casual videos often influence decisions because they feel unscripted and honest, even when they are simple or imperfect.
Platforms also play a role. Social networks are designed to surface content that looks native and encourages interaction. UGC fits this environment better than highly produced content, which is why it often performs well in feeds, recommendations, and search results.
Finally, UGC is popular because it is accessible. Anyone can create it without special tools or training. This has turned everyday users into creators and made UGC one of the most widespread and influential forms of content online today.
Types of User-Generated Content
User-generated content comes in many forms, but all of it shares one thing in common: it is created by people, not companies. Understanding the main types helps clarify where UGC appears and how it’s commonly used online.
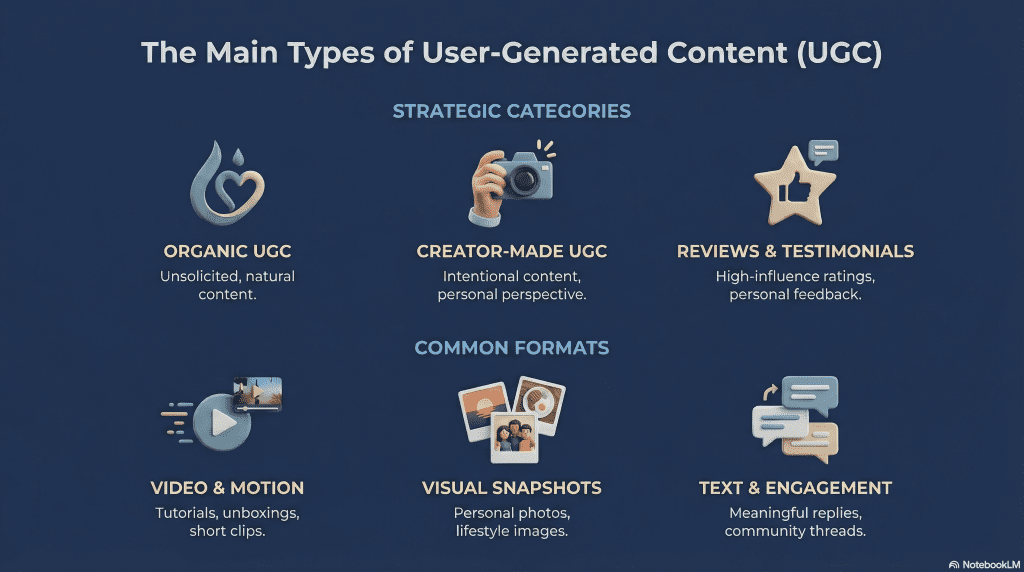
Organic UGC
Organic UGC is content people create naturally, without being asked or paid. This includes social media posts, comments, reviews, forum replies, and videos shared simply because someone wanted to express an opinion or experience. It’s the most common form of UGC and often the most trusted because it’s unsolicited.
Creator-Made UGC
Creator-made UGC is produced intentionally by individuals who understand content creation. This type often looks more structured or higher quality, but it is still created from a personal perspective rather than a brand voice. It can appear on social platforms, blogs, or video sites and may or may not involve compensation.
Review and Testimonial UGC
Reviews and testimonials are a classic form of UGC. They include written reviews, star ratings, video reviews, and before-and-after experiences. These are especially influential because they directly reflect real outcomes and opinions.
Video, Image, and Text-Based UGC
UGC can be:
- Video, such as short-form clips, tutorials, or reactions
- Images, like photos, screenshots, or visual posts
- Text, including reviews, comments, captions, and long-form posts
Each format plays a different role, but all contribute to how ideas and information spread online.
How to Do User-Generated Content (UGC)
User-generated content is created by doing, not by planning endlessly. The process is simple, but each step matters if you want your content to feel natural and useful.
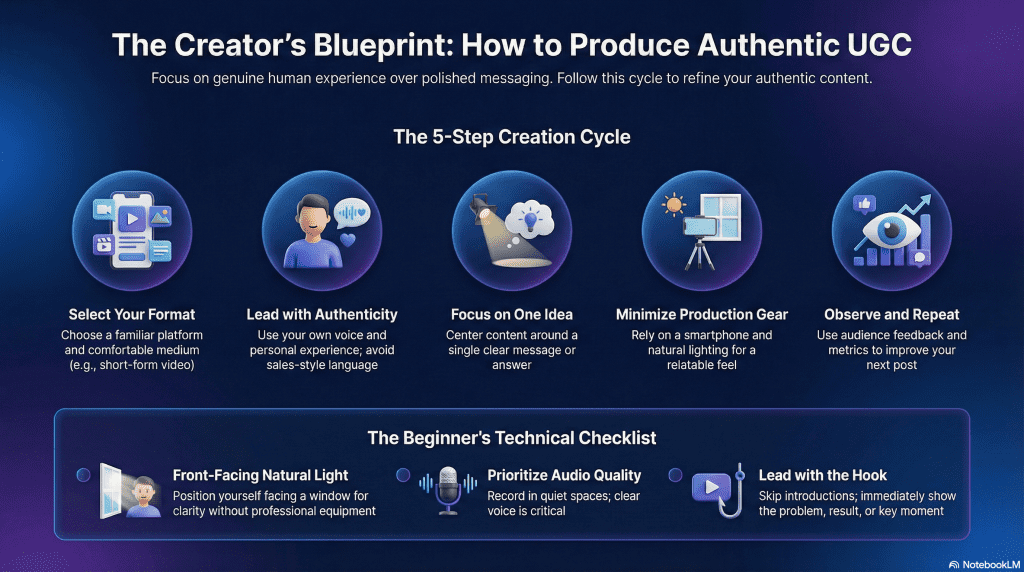
Choose a Platform and Content Format
Start with a platform you’re already comfortable using. Short-form video is the most common UGC format today, but photos, written posts, and simple tutorials also qualify. Choose one format so you can focus on communication instead of learning new tools.
Create Content From a Real User Perspective
UGC works best when it reflects genuine experience. Show how something is used, explain what you like or don’t like, or walk through a real situation. Speak in your own words and avoid rehearsed or sales-style language.
Focus on One Clear Idea
Each piece of UGC should communicate a single point. This could be demonstrating a feature, answering a common question, or sharing a quick opinion. Clear, focused content is easier to follow and more effective than trying to cover everything at once.
Keep Production Simple and Natural
You don’t need professional lighting, editing, or scripts. A phone, natural light, and clear audio are enough. Slight imperfections often make UGC feel more authentic and relatable.
Publish, Observe, and Repeat
Post your content and pay attention to how people respond. Notice what gets watched, commented on, or shared. Use that feedback to improve the next piece. Consistency builds skill and confidence over time.
Creating UGC is a repeatable process. The more you practice these steps, the more natural and effective your content becomes.
The Beginner’s UGC Checklist
You don’t need professional equipment to create UGC, but a few basics make a big difference. Before you record or publish, check these fundamentals.
- Lighting: Make sure the light source is in front of you. Natural light from a window works well. Avoid standing with your back to the light.
- Audio: Your voice should be clear and easy to understand. Poor audio distracts faster than imperfect video, so record in a quiet space.
- The Hook: Start with the most interesting part. Skip introductions and lead with the problem, result, or key moment.
UGC works because it feels real. When content looks too polished or staged, it starts to feel like an ad, which defeats the purpose.

Real Examples of User-Generated Content
User-generated content isn’t abstract, it’s everywhere online. Once you know what to look for, you’ll start noticing it across platforms and formats.
Social Media Posts and Videos
Short videos on platforms like TikTok, Instagram, or YouTube where people share opinions, routines, reactions, or experiences are classic UGC. These posts feel casual because they are created in a personal voice, not a brand one.
Reviews and Ratings
Product reviews, star ratings, and written feedback on marketplaces, app stores, and forums are some of the oldest and most influential forms of UGC. People rely on them to validate decisions before taking action.
Tutorials, Demos, and How-To Content
Walkthroughs, unboxings, and “how I use this” videos are UGC because they show real use from a real person’s perspective. These examples often influence behavior more than official explanations.
Comments, Threads, and Community Posts
Replies on social platforms, discussion boards, and community spaces also count as UGC. Even short comments contribute to how opinions form and spread online.
How User-Generated Content Works in Practice
User-generated content works because it follows a natural cycle that already exists online. People create content based on real experiences, platforms distribute it through feeds and search, and audiences decide what spreads by how they engage with it. There is no formal launch or promotion process, the system runs on everyday behavior.
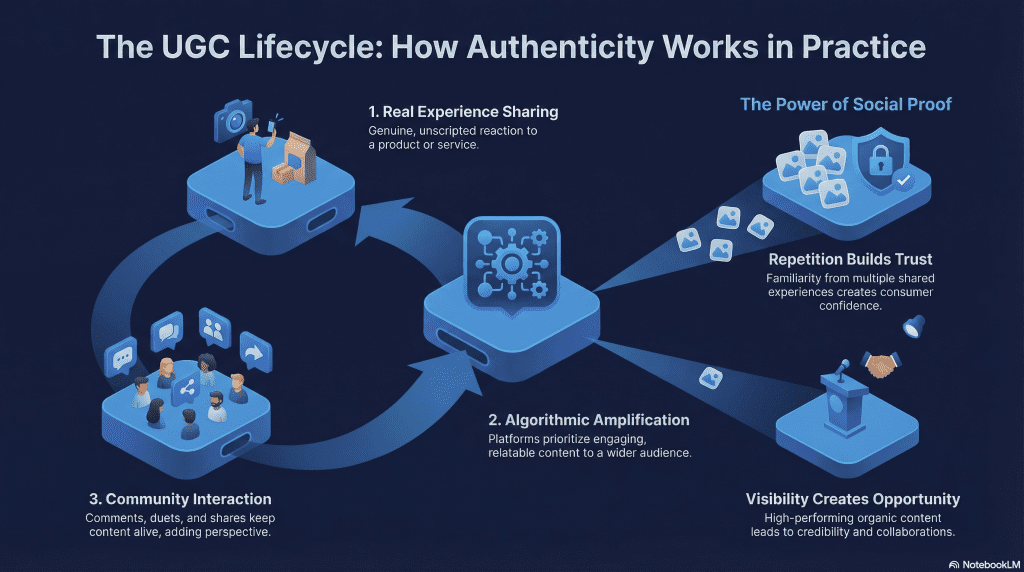
It Starts With Real People Sharing Real Experiences
UGC begins when someone documents, explains, or reacts to something they’ve used, tried, or noticed. This could be a quick opinion, a walkthrough, or a casual observation. Because the content is personal and unscripted, it feels believable and easy to connect with.
Platforms Surface What Holds Attention
Social platforms and search engines prioritize content that keeps people watching, reading, or interacting. When UGC generates views, comments, saves, or shares, it signals relevance. The platform responds by showing that content to more users, extending its reach beyond the original audience.
Repetition Builds Familiarity and Trust
UGC becomes more influential as similar content appears repeatedly. Seeing different people share comparable experiences around the same topic builds familiarity. Over time, that familiarity turns into trust, even without direct persuasion.
Interaction Keeps Content Alive
Comments, replies, stitches, duets, and follow-up posts create momentum. Each interaction adds context, answers questions, or introduces new perspectives. This keeps the content active and visible while encouraging others to contribute their own UGC.
Visibility Creates Opportunity
As UGC spreads, it can lead to attention, credibility, or opportunities tied to the creator or topic. Content that performs well often becomes a reference point that others discover later through search or recommendations.
In practice, UGC works because it fits how people already behave online: sharing experiences, responding to others, and building meaning through repeated interaction.
UGC vs Influencer Content
UGC and influencer content are often confused, but they are not the same thing. The difference comes down to purpose and focus, not popularity.
UGC is about the content itself.
It’s created from a personal point of view and stands on its own, regardless of how many followers the creator has. The value comes from authenticity and relatability.
Influencer content is about the audience.
Influencers are chosen primarily for their reach. Their content is tied to distribution and visibility rather than just the message or experience being shared.
Key Differences
- Audience size: UGC does not require a following; influencer content usually does
- Focus: UGC centers on experience; influencer content centers on promotion
- Tone: UGC feels natural and casual; influencer content is often more intentional
- Use case: UGC blends into feeds and conversations; influencer content is more campaign-driven
Because of this, someone can create UGC without being an influencer, and an influencer can create content that is not considered true UGC. Understanding the difference helps clarify why the two serve different roles online.
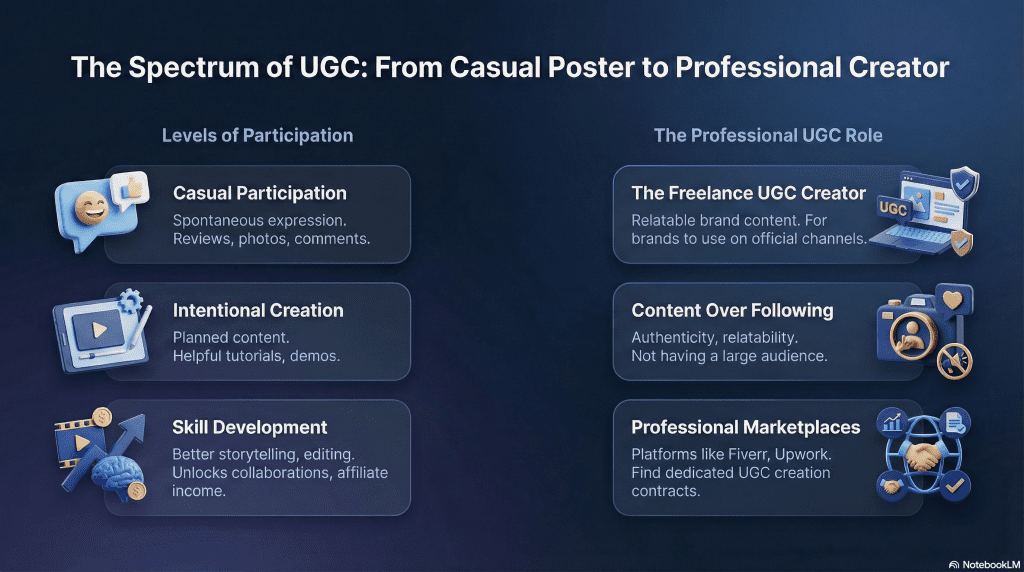
How People Get Involved With UGC
People get involved with user-generated content in different ways, depending on interest, skill level, and goals. There is no single path, which is part of what makes UGC so accessible.
Casual Participation
Many people create UGC without planning to. Posting a review, sharing a photo, leaving a comment, or uploading a short video are all forms of casual UGC. This type of participation is driven by expression, not strategy.
Intentional Creation
Others create UGC on purpose. They plan content, choose platforms, and focus on clarity or usefulness. This often includes tutorials, demonstrations, opinions, or explanations designed to be helpful or engaging.
Skill Development and Opportunities
Over time, some people treat UGC as a skill. They improve storytelling, on-camera presence, and editing. This can lead to opportunities such as collaborations, affiliate income, or paid content creation, even without a large audience.
UGC doesn’t require credentials or permission. Anyone can start creating, learn by doing, and decide how far they want to take it.
The Rise of the UGC Creator Role
As UGC has grown, it has also created a new freelance role often referred to as the UGC creator. Unlike influencers, UGC creators are not paid to post content on their own channels. Instead, they are hired to create videos or other content that brands can use on their own platforms.
This model focuses on content creation rather than audience size. Someone can produce effective UGC without having a large following, as long as the content feels natural and relatable. As a result, marketplaces and freelance platforms like JoinBrands, Fiverr, and Upwork have introduced categories specifically for UGC-style content creation.
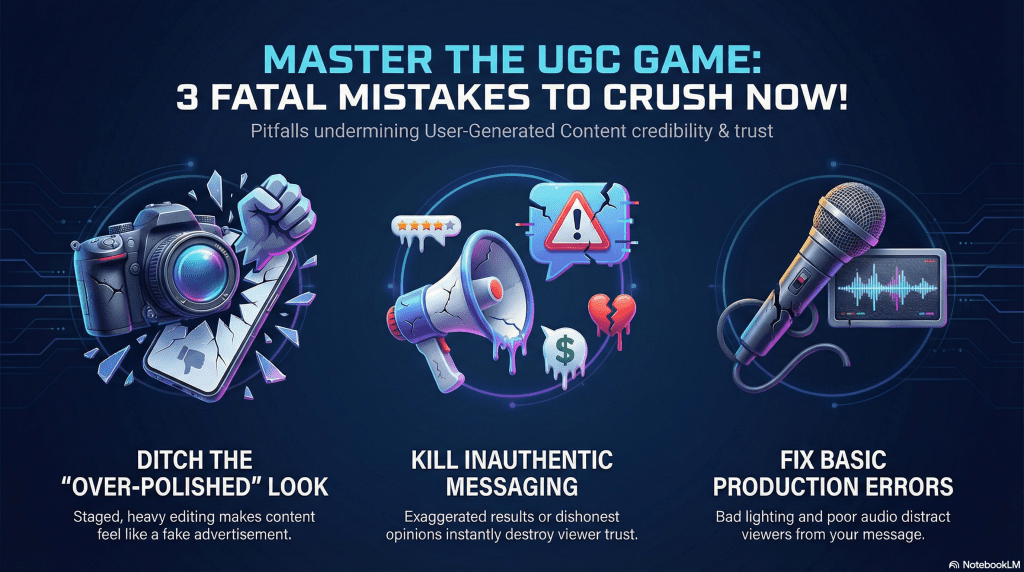
What to Avoid or Watch Out for With UGC
User-generated content is simple, but small missteps can undermine its impact. Knowing what to avoid helps keep UGC effective, credible, and sustainable.
Trying to Make It Look Too Perfect
UGC loses its value when it starts to feel staged. Heavy editing, scripted delivery, or overly polished visuals can make content look like an ad. Slight imperfections often make UGC feel more believable and relatable.
Copying Trends Without Context
Trends change quickly, and not all of them fit every topic or creator. Copying a format without understanding why it works can lead to content that feels forced. Focus on whether the trend supports your message, not just whether it’s popular.
Ignoring Basic Quality Standards
UGC doesn’t require professional production, but it should still be easy to watch or read. Poor audio, bad lighting, or unclear explanations distract from the message and cause people to scroll past.
Being Misleading or Inauthentic
UGC depends on honesty. Exaggerating results, hiding context, or presenting opinions you don’t actually believe can damage trust. Even small inconsistencies can make content feel unreliable.
Overlooking Ownership and Permissions
By default, the creator owns their content. Problems can arise when UGC is reused, reposted, or monetized without clear permission. Understanding basic rights and usage rules helps avoid conflicts later.
Expecting Instant Results
UGC rarely works overnight. Creating effective content takes practice and repetition. Expecting immediate visibility or outcomes can lead to frustration or burnout.
UGC works best when it stays honest, clear, and grounded in real experience. Avoiding these pitfalls keeps the focus where it belongs, on genuine content that people trust.

Conclusion
User-generated content is not a trend or a tactic, it’s a fundamental part of how the internet works today. It exists because people prefer real experiences, real opinions, and real voices over polished messages. Understanding what UGC is, where it appears, and why it matters helps remove the confusion around the term.
UGC shows up naturally across platforms through posts, videos, reviews, and conversations. Anyone can create it, intentionally or casually, and its influence comes from authenticity rather than production quality. This is why it continues to shape how information spreads and how attention is earned online.
By understanding UGC at a foundational level, you’re better prepared to recognize opportunities around it, whether that’s creating content, building skills, or exploring ways it fits into broader digital activity. Clarity is the first step before action.

Frequently Asked Questions
What qualifies as user-generated content (UGC)?
UGC is any content created by individuals rather than brands or companies. This includes videos, photos, reviews, comments, posts, and tutorials shared online.
Is user-generated content always unpaid?
No. Most UGC is unpaid, but some creators are compensated or monetize their content. Payment does not determine whether content is considered UGC.
Do you need followers to create UGC?
No. UGC is about the content itself, not audience size. Anyone can create UGC regardless of how many followers they have.
Is UGC the same as influencer content?
No. Influencer content focuses on reach and audience size, while UGC focuses on authentic content created from personal experience.
Who owns user-generated content?
The person who creates the content owns it by default, unless rights are granted or transferred through an agreement.
0 Comments