Introduction: Why One Prompt Often Isn’t Enough
Multi-Chain Prompting exists for a simple reason: some tasks are too complex to solve in a single prompt.
When you ask an AI to analyze, plan, write, and refine all at once, you’re forcing it to make decisions it hasn’t earned yet. The result is usually shallow, generic, or slightly off, not because the AI is weak, but because the instruction is overloaded.
Multi-Chain Prompting takes a different approach. Instead of asking for a finished answer immediately, you guide the AI through a sequence of smaller, focused prompts. Each step builds on the last, allowing the model to think in stages rather than guessing everything at once.
In this article, you’ll learn what Multi-Chain Prompting is, why it works so well for complex tasks, and how to use it to get clearer, more accurate results without overengineering your prompts.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-Chain Prompting breaks complex tasks into manageable steps. Instead of forcing one prompt to do everything, you guide the AI through a clear sequence of focused actions.
- Single prompts fail when thinking and execution are mixed. Separating clarification, decision-making, and output leads to more accurate and structured results.
- Each prompt should have one job. One step to clarify, one to decide, one to produce is often enough.
- Reviewing between steps gives you control. Fixing issues early is faster than rewriting a final output.
- Multi-Chain Prompting is proactive, not reactive. It prevents problems instead of patching them with follow-up prompts.
- The approach scales with complexity. The more nuanced the task, the more value you get from chaining prompts.
- Saved chains become reusable workflows. Over time, Multi-Chain Prompting turns into a system that consistently saves time and improves quality.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.
What Is Multi-Chain Prompting in LLMs
Multi-Chain Prompting is a technique where a task is broken into multiple, sequential prompts, with each response feeding into the next step. Instead of asking a large language model (LLM) to handle everything at once, you guide it through a series of smaller, focused actions.
In LLMs, this approach works because the model performs better when it can concentrate on one objective at a time. Each prompt narrows the scope, reduces ambiguity, and creates a clearer decision path for the next step. The output becomes more structured, accurate, and aligned with your intent.
You may see this concept discussed alongside terms like “chain-of-thought prompting.” While related, Multi-Chain Prompting is less about exposing the model’s internal reasoning and more about designing a practical workflow. The emphasis is on iteration and control, not on getting a single “perfect” prompt.
In simple terms, Multi-Chain Prompting means building the answer step by step instead of hoping one prompt does all the thinking for you.
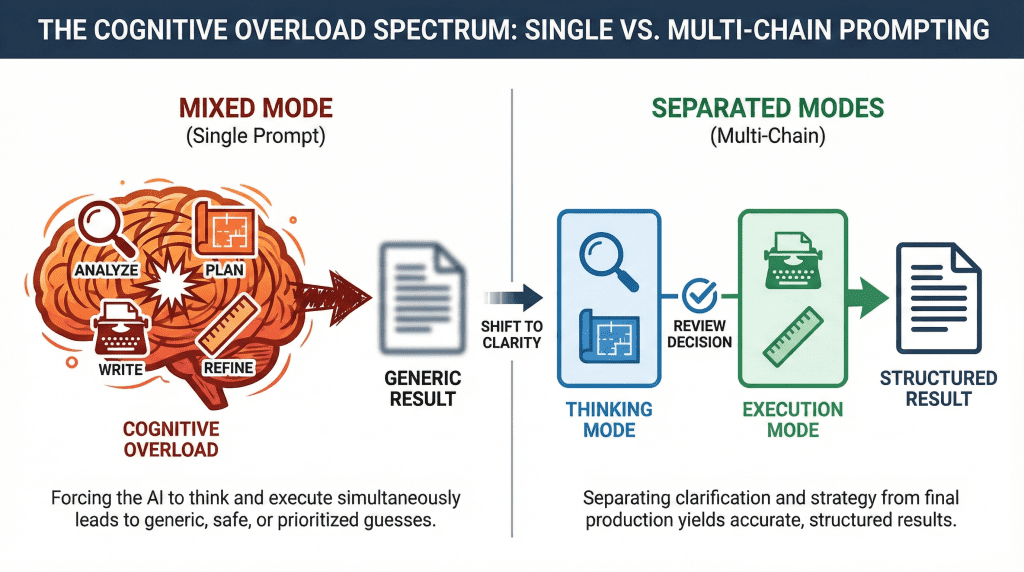
Why Single Prompts Fail for Complex Tasks
Single prompts work well for simple requests. But once a task involves multiple decisions, trade-offs, or layers of thinking, a single prompt often breaks down.
The first issue is cognitive overload. When an AI is asked to analyze information, apply strategy, write polished output, and follow constraints all at once, it has to prioritize. Important details get lost, and the response defaults to safe, generic patterns.
The second issue is conflicting goals. A prompt that asks the model to be creative, concise, persuasive, and highly accurate at the same time gives it no clear path forward. The result usually satisfies none of those goals particularly well.
Finally, single prompts leave little room for correction. If the output misses the mark, you’re forced to rewrite the entire instruction instead of adjusting one specific part. This turns prompting into trial and error rather than a controlled process.
Multi-Chain Prompting avoids these problems by separating thinking into steps. Each prompt has a single responsibility, which makes the output easier to evaluate, refine, and build on in the next stage.
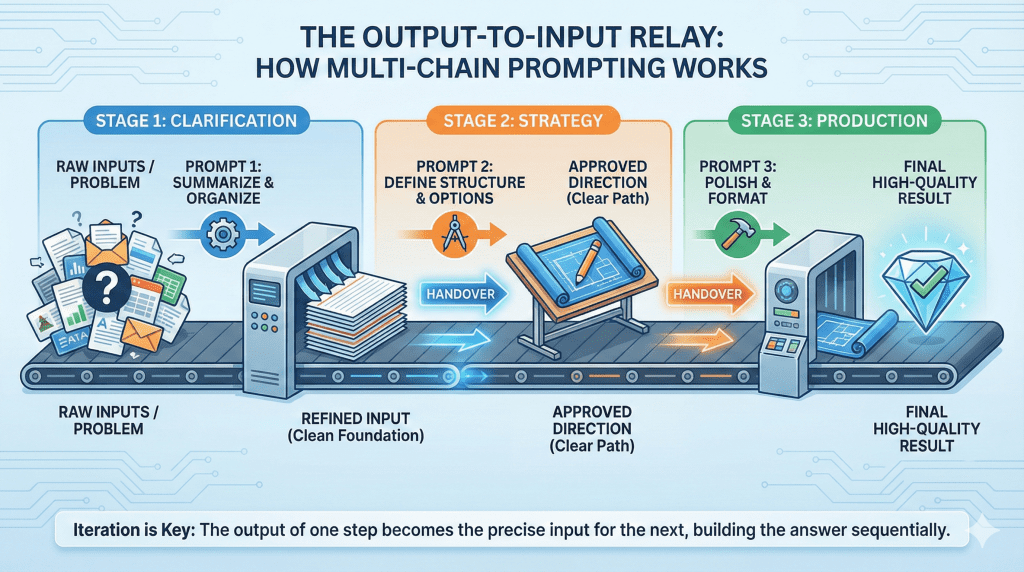
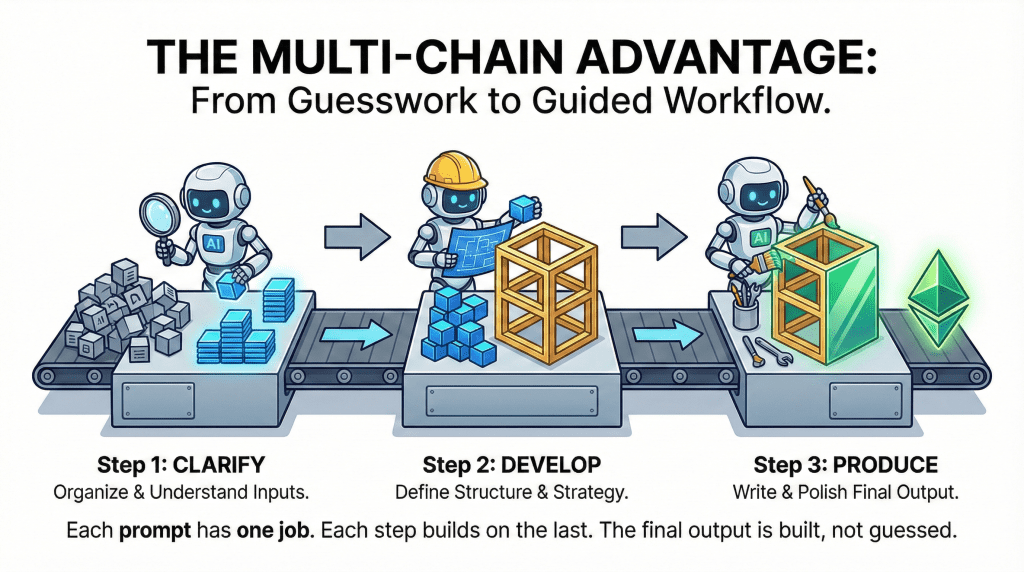
How Multi-Chain Prompting Actually Works
Multi-Chain Prompting works by shifting your mindset from “get the final answer” to “build the answer.”
Instead of asking the AI to analyze, decide, and produce everything in one step, you divide the task into a logical sequence of smaller actions. Each prompt has a single, well-defined objective, and the output from that step becomes the input for the next. This reduces ambiguity and gives the model a much clearer path forward.
A typical multi-chain flow looks like this:
- Clarify the problem or inputs – ask the AI to summarize, extract, or organize raw information so the foundation is clean and accurate.
- Develop structure or direction – use that refined input to identify options, define strategy, or outline the approach.
- Produce the final output – write, format, or polish the result based on decisions already made upstream.
The key advantage of this approach is control. After each step, you can evaluate the output before moving on. If something feels off, you adjust one prompt instead of starting over. This makes the process more predictable and far less frustrating.
In practice, Multi-Chain Prompting feels closer to collaboration than command. You guide the thinking, step by step, while the AI focuses on executing each task well. The final output is not the result of a single guess, but the accumulation of clear, intentional choices made along the way.
Multi-Chain Prompting vs Follow-Up Prompts
Multi-Chain Prompting and follow-up prompts may look similar on the surface, but they solve very different problems.
Follow-Up Prompts
Follow-up prompts are reactive. You start with a single broad instruction, review the output, then ask the AI to fix or adjust what didn’t work.
This approach is useful when:
- The task is simple or exploratory
- You’re not sure what you want yet
- Small refinements are enough
However, follow-ups often lead to:
- Repeating yourself
- Accumulating conflicting instructions
- Losing clarity as the thread gets longer
You’re essentially patching the output instead of shaping it from the start.
Multi-Chain Prompting
Multi-Chain Prompting is intentional and structured. You design the sequence before you begin, with each prompt responsible for one clear step.
This approach works best when:
- The task has multiple layers or decisions
- Accuracy and structure matter
- You want consistent, repeatable results
Instead of fixing mistakes later, you prevent them by narrowing the scope at each stage.
The Key Difference
| Aspect | Follow-Up Prompts | Multi-Chain Prompting |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Reactive | Proactive |
| Timing | Fixes output after the fact | Guides thinking step by step |
| Workflow | One broad prompt, then patches | Planned sequence of focused prompts |
| Feel Over Time | Can feel messy over time | Stays clean and controlled |
| Best Use | Best for quick tweaks | Best for complex tasks |
How to Choose
If you’re experimenting or brainstorming, follow-up prompts are often enough.
If the task needs structure, clarity, or precision, Multi-Chain Prompting will save time and reduce frustration.
Think of follow-ups as edits. Think of multi-chain prompting as a workflow.
Real Examples of Multi-Chain Prompting Workflows
Multi-Chain Prompting becomes most useful when you see how it applies to real tasks. Below are practical workflows that show how breaking a task into steps produces clearer, more reliable results than a single prompt ever could.
Content Creation Workflow
Goal: Produce a high-quality article or post without rewriting everything.
Clarify the source material Prompt the AI to summarize or extract the key ideas from your notes, transcript, or rough draft.
Shape the message Use the summary to define the angle, audience, and structure. Ask for an outline or key talking points.
Write the final draft Generate the content using the approved structure and messaging decisions from earlier steps.
Why this works: The AI isn’t guessing what matters. Each step locks in decisions before writing begins.
Strategy & Planning Workflow
Goal: Make a decision that involves trade-offs or constraints.
Define the problem and constraints Ask the AI to restate the problem, goals, and limitations based on your input.
Generate options Have the AI propose multiple approaches that fit within those constraints.
Evaluate and compare Ask the AI to assess pros, cons, risks, or second-order effects of each option.
Why this works: You separate ideation from evaluation, which leads to more thoughtful recommendations.
Analysis & Research Workflow
Goal: Turn large amounts of information into clear insights.
Organize the data Ask the AI to summarize documents, extract patterns, or categorize inputs.
Identify insights Prompt the AI to highlight trends, anomalies, or key takeaways.
Produce recommendations Use those insights to generate conclusions, next steps, or executive summaries.
Why this works: Each step narrows the focus, reducing noise and improving accuracy.
Communication Workflow (Email or Support)
Goal: Send a clear, well-toned message with minimal revision.
Clarify intent Ask the AI to restate what the message needs to accomplish and what tone is appropriate.
Draft the message Generate the response using the clarified intent and tone.
Polish and shorten Refine for clarity, brevity, or professionalism.
Why this works: Tone, intent, and wording are handled separately, preventing mixed signals.
These workflows show the core advantage of Multi-Chain Prompting: each prompt does one job well. By the time you reach the final step, most of the thinking is already done, and the output reflects a clear, deliberate process rather than a rushed guess.
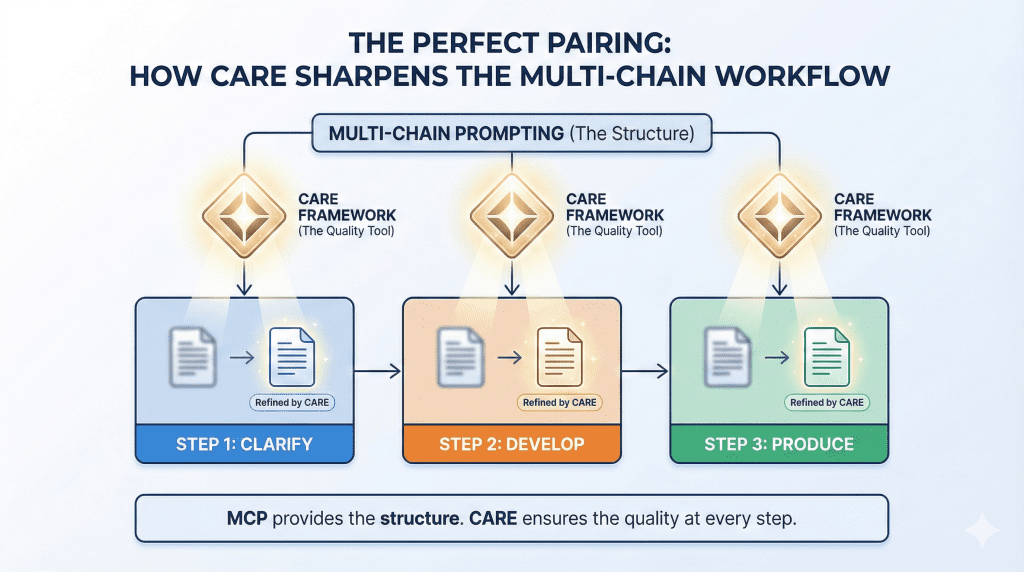
How Multi-Chain Prompting Pairs With the CARE Framework
Multi-Chain Prompting and the CARE framework solve different problems, but they work best together.
Multi-Chain Prompting focuses on how a task is broken down over time. It helps you decide what comes first, what comes next, and what depends on previous decisions. CARE, on the other hand, improves the quality of each individual prompt inside that chain.
Think of it this way:
- Multi-Chain Prompting designs the workflow
- CARE sharpens each step in that workflow
When combined, you get both structure and clarity.
For example, in a three-step multi-chain process:
- Clarify inputs. Use CARE to provide context about the source material, clearly ask for a summary, set rules for length, and include an example if tone matters.
- Develop direction. Apply CARE again to define the task, add constraints, and guide how options or strategies should be presented.
- Produce the final output. CARE ensures the final draft follows the right tone, format, and level of detail.
This pairing prevents two common problems. First, it stops multi-chain workflows from becoming vague or inconsistent between steps. Second, it prevents well-written prompts from being wasted inside a poorly planned process.
Used together, CARE improves prompt quality, and Multi-Chain Prompting improves thinking quality. The result is output that is not only better written, but better reasoned.

When to Use Multi-Chain Prompting (And When Not To)
Multi-Chain Prompting is most valuable when the task requires structure, judgment, or multiple decisions. If the outcome matters and you want the first usable result without heavy editing, breaking the work into steps is usually worth the extra prompts.
You should use Multi-Chain Prompting when:
- The task has multiple layers, such as analysis, strategy, and execution
- Accuracy and clarity matter more than speed
- You’re making decisions with trade-offs or constraints
- You plan to reuse the workflow for similar tasks in the future
In these cases, chaining prompts saves time overall by reducing confusion and rework.
However, Multi-Chain Prompting isn’t necessary for everything.
For simple tasks like brainstorming ideas, quick summaries, or informal drafts, a single prompt is often enough. Adding multiple steps in those situations can slow you down without improving the result.
A practical rule of thumb is this: If the task requires thinking before writing, use Multi-Chain Prompting. If it only requires generating content, keep it simple.

How to Start Using Multi-Chain Prompting Without Overthinking
You don’t need a complex system or a perfectly planned workflow to start using Multi-Chain Prompting. The goal is not to add friction, but to reduce it by making each step clearer and easier to control.
Identify the Real Outcome
Before writing any prompt, decide what a “good” final result looks like. Are you trying to make a decision, write something polished, or extract insight? This prevents you from jumping straight into generation without direction.
Break the Task Into Thinking and Doing
Separate prompts that require reasoning from prompts that require execution. For example, clarifying ideas, evaluating options, or choosing an angle should happen before writing or formatting anything.
Start With a Clarification Prompt
Use the first prompt to clean up inputs. Ask the AI to summarize, organize, or restate the information you’re working with. This step creates a solid foundation and reduces errors later in the chain.
Make One Decision Per Prompt
Each prompt should have a single responsibility. One step might define structure. Another might compare options. Another produces the final output. Avoid stacking decisions in one instruction.
Review Before Moving Forward
After each step, quickly scan the output. If something feels off, fix it immediately before continuing. Adjusting one step is faster than reworking the entire chain later.
Keep Chains Short and Purposeful
Most tasks only need two to four steps. If the chain starts feeling bloated, ask whether each step is truly necessary or if it can be simplified.
Save What Works
When a multi-chain sequence consistently produces good results, save it. Over time, you’ll build a library of repeatable workflows that make complex tasks faster and more predictable.
Multi-Chain Prompting becomes powerful when it’s treated as a habit, not a technique. Small, intentional steps compound into clearer thinking and better output.
Conclusion: Better Results Come From Better Steps
Multi-Chain Prompting works because it matches how real thinking happens.
Complex tasks are rarely solved in one jump. They require clarification, decisions, and refinement before a final answer makes sense. When you try to compress all of that into a single prompt, the AI is forced to guess. Multi-Chain Prompting removes that guesswork by guiding the process step by step.
This approach doesn’t require longer prompts or technical knowledge. It simply asks you to slow down the thinking so the AI can keep up. By giving each prompt a single job and reviewing the output before moving on, you gain control over both the process and the result.
You don’t need to use Multi-Chain Prompting for everything. Start with one task that keeps producing mediocre results. Break it into two or three steps. Notice how much clearer and more reliable the output becomes.
Better AI results aren’t about finding the perfect prompt. They come from building better steps.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is Multi-Chain Prompting?
Multi-Chain Prompting is a technique where you break a complex task into a sequence of smaller prompts, with each response feeding into the next. This allows the AI to focus on one step at a time instead of guessing everything in a single prompt.
Is Multi-Chain Prompting the same as chain-of-thought prompting?
They are related but not the same. Chain-of-thought focuses on exposing the model’s reasoning process, while Multi-Chain Prompting focuses on structuring your workflow. The goal is better results through step-by-step guidance, not revealing internal reasoning.
How many steps should a multi-chain prompt have?
Most tasks work best with two to four steps. If a chain becomes too long, it’s usually a sign that some steps can be combined or simplified.
Do I need to label each step when using Multi-Chain Prompting?
No. Labels are optional. What matters is that each prompt has a clear purpose. Many people use the framework mentally rather than writing out step names explicitly.
When should I avoid Multi-Chain Prompting?
For simple tasks like brainstorming ideas or quick summaries, a single prompt is often enough. Multi-Chain Prompting is best reserved for tasks that require structure, judgment, or accuracy.
Can Multi-Chain Prompting be used with any AI tool?
Yes. Multi-Chain Prompting works with ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other large language models because it relies on how instructions are given, not on tool-specific features.
Does Multi-Chain Prompting slow things down?
At first, it may feel slower because you’re writing more than one prompt. In practice, it usually saves time by reducing rewrites, confusion, and trial-and-error.
0 Comments